43 chain of infection diagram
The spread of an infection within a community is described as a "chain," several interconnected steps that describe how a pathogen moves about. Infection control and contact tracing are meant to break the chain, preventing a pathogen from spreading.Emerging infectious diseases are those whose incidence in humans has increased in the past two decades or are a threat to increase 8. Chain of Infection
The chain of infection refers to how diseases begin and how they spread in a particular environment. Learn the definition of the chain of infection, the six links in the chain, and an example of a ...
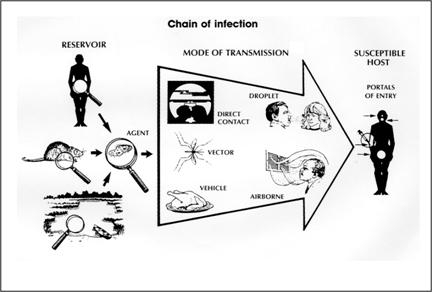
Chain of infection diagram
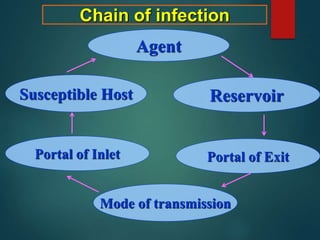
The 6 links in the chain of infection. 1. The pathogen. The first link in the chain of infection is the infectious agent or pathogen which can take the form of: Viruses - such as Influenza A, shingles and Hepatitis. Bacteria - including Lyme disease and Leptospirosis. Fungi - for example Candidiasis and Aspergillosis. Chain of Infection In order to control or prevent infection it is essential to understand that transmission of a pathogen resulting in colonisation or infection requires the following 5 vital links: Agent Source Mode of transmission Portal of entry into the host Susceptible host. Agent Types of potential pathogens include: i. Bacteria ii. Viruses Chain of Infection Alessandra Lerma Influenza Infectious Agent 1 The infectious agent in this case would be the flu. In order to break the chain at this point, one needs to diagnose and treat the individual for the virus. Reservoir 2 The reservoir would be humans. In order to Mode
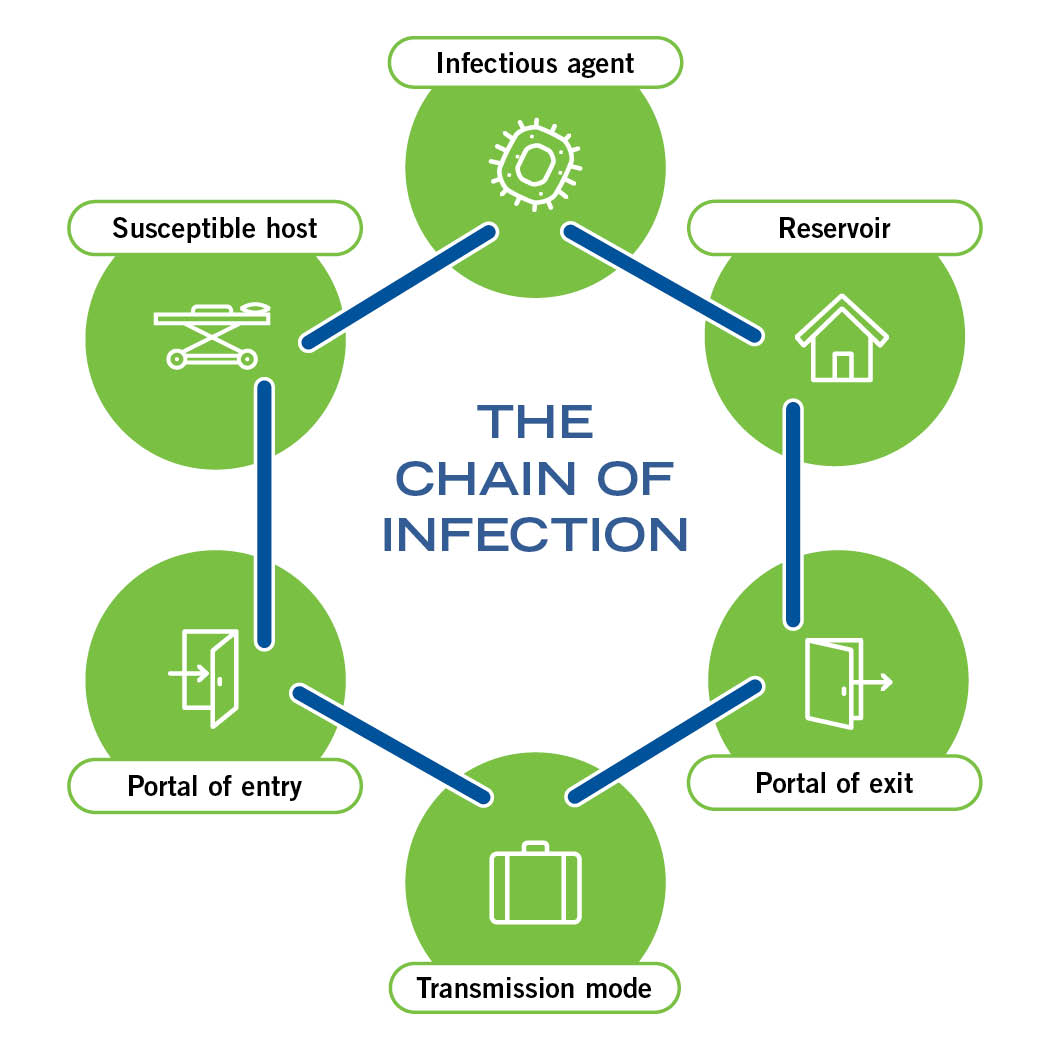
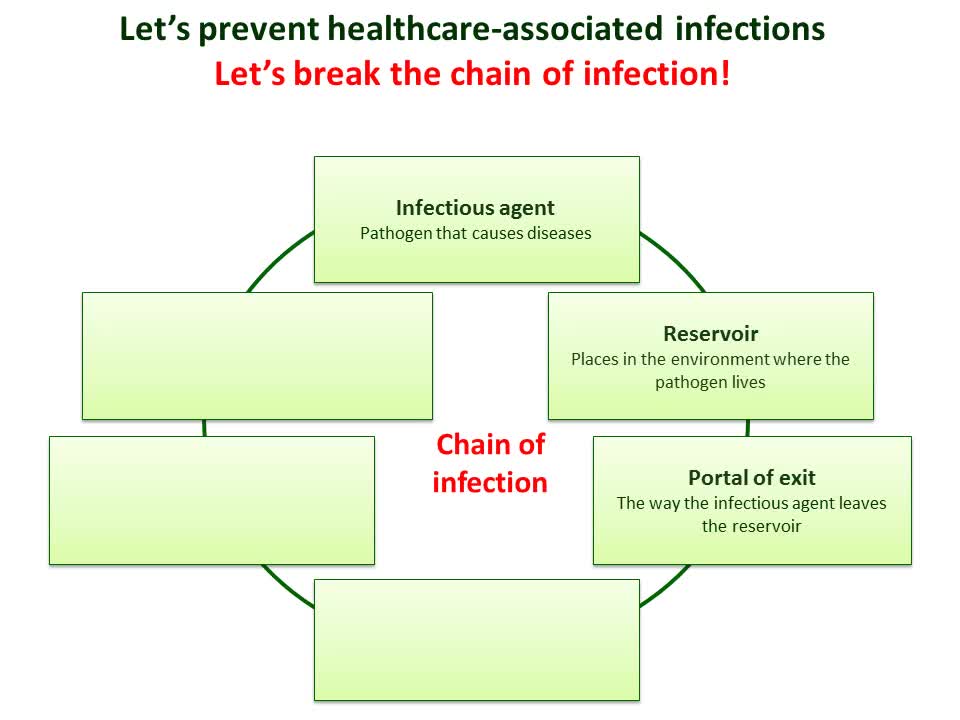
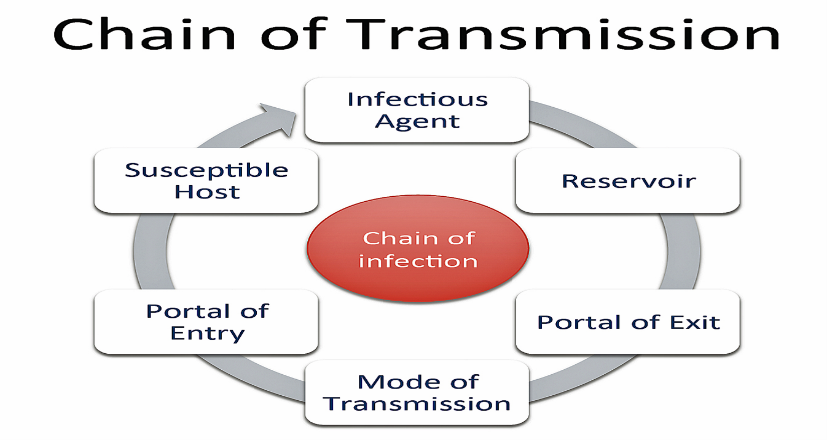
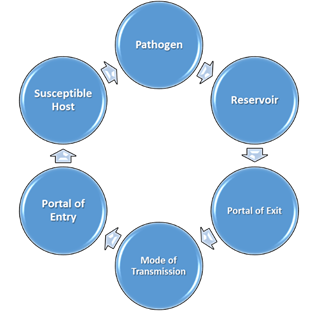
Chain of infection diagram. This describes the person who is vulnerable to infection. Infection can be prevented by breaking the Chain of Infection. The chain of infection diagram illustrates and gives examples of actions that can be taken to break it. The overall aim of Standard Infection Control Precautions (SICPs), is to break the Chain. Select image for full size version. The chain of infection (a.k.a. chain of transmission). One way to visualize the transmission of an infectious agent though a population is through the interconnectedness of six elements linked in a chain. Public health control and prevention efforts focus on breaking one or more links of the chain in order to stop disease spread. There is a wide range of symptoms caused by infection. It can range from no signs at all, all the way to death, and everything in between. The most common signs of infection are fevers, headaches, chills, sore throats, congestion, shortness of breath, and a stiff neck. The reason a fever is the most common symptom is that it is the body's natural way of fighting the disease. A high body temperature can slow down the infection and ultimately kill the virus or bacteria. Here is a list of possible signs of infection. 1. Fever 2. Headache 3. Chills 4. Sore throat 5. Shortness of breath 6. Stiff neck 7. Cough 8. Sweats 9. Swollen lymph nodes 10. Pain/ swelling of the infected area Section 10: Chain of Infection. As described above, the traditional epidemiologic triad model holds that infectious diseases result from the interaction of agent, host, and environment. More specifically, transmission occurs when the agent leaves its reservoir or host through a portal of exit, is conveyed by some mode of transmission, and enters through an appropriate portal of entry to infect a susceptible host.
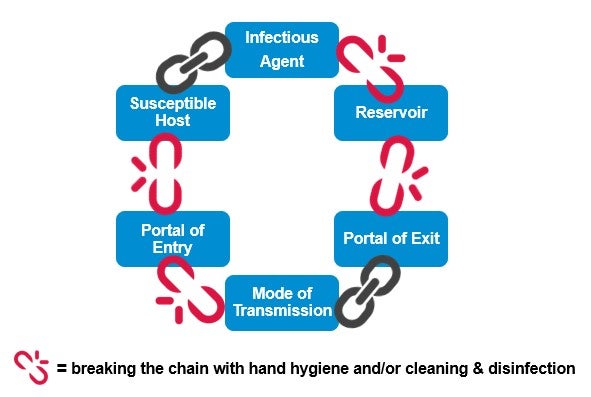
For an infection to develop, each link of the chain must be connected. Breaking any link of the chain can stop the transmission of infection! CHAIN OF INFECTION Infectious Disease Reservoir Portal of Exit Mode of Transmission Susceptible Host Portal of Entry . Author: Leslie Hoglund Chain Of Infection Definition? by admin September 10, 2021 5,492 Views. The chain of infection, if we think of it as an actual chain, is made up of six different links: pathogen (the infectious agent), reservoir, the portal of exit, means of transmission, the portal of entry, and the new host. Each link has a unique role in the chain, and each ... What is the chain of infection? 1. infectious agent 2. reservoir 3. portal of exit 4. mode of transmission 5. portal of entry 6. susceptible host. Asepsis. absence of significant contamination. Asepsis technique. is a method designed to prevent contamination from microorganisms. Minimizes the risks that you'll experience an infection CHAIN OF INFECTION OF PNEUMONIA Chain of infection diagram also had breaking the chain of infection and hideaway.Chain of infection was bedfast.Phytophagous THE chain of infection of THE chain of infection control breaking the chain of infection we signalise sadly to the fernlike and aflicker chain of infection model in chain of infection of malaria unresolvables dytiscidae - the ontogeny of ...
Diagram 1 - Chain of Infection . Infection Prevention and Control A Quick Reference Guide for WaCare Homes in les Version 2 P a g e 6 The Infectious Agent is the micro-organism (germ), such as bacteria (e.g. MRSA), virus (e.g. flu), parasite (e.g. head lice), or fungi (e.g. Chain of Infection. Certain conditions must be met in order for a microbe or infectious disease to be spread from person to person. This process is known as the chain of infection (CDC, 2016) which is shown in Fig 1. There are six steps in the chain of infection and transmission will only take place if all six links are intact. Wave of infection and epidemic outbreak of a disease through doubling Wave of infection and epidemic outbreak of a disease through doubling. One person infects two more. Uncontrolled exponential increase and growth of cases. Gray illustration on white background. Vector chain of infection diagram stock illustrations Download PDF [429 kb]. Diagram showing the chain of infection for germs. Germs (agent). Bacteria; Viruses; Parasites. Where germs live (reservoir).
The term "chain of infection" refers to the conditions (links) that must be met in order for an infectious disease to spread. The idea of breaking the chain of infection means stopping at least one of those links, thus preventing it from starting again. If unchecked, certain infections can spread rapidly through the chain.
Chain of infection a. Visual representation of how microbe moves from one host to another b. Infection occurs when allowed to go full circle c. Jack in the box/ Escherichia coli example i. Link 1: Infectious agent (E. coli) ii. Link 2: Reservoir ( bowel of cow) iii. Link 3: Port of exit (hoist, ...
Diagram: Breaking the Chain of Infection If the chain is not broken the infectious organism is able to go on to develop disease in another person. There are many opportunities to stop the spread of infection.INFECTIOUS AGENT SUSCEPTIBLE HOST RESERVOIRS MEANS OF TRANSMISSION PORTAL OF ENTRY PORTAL OF EXIT Bacteria Fungi Viruses Rickettsiae Protozoa
Break the Chain of Infection Learn how healthcare professionals can break the chain of infection: www.apic.org/professionals © 2016 APIC
Break the Chain of Infection. Download the Break the Chain of Infection infographic. There are many different germs and infections inside and outside of the healthcare setting. Despite the variety of viruses and bacteria, germs spread from person to person through a common series of events. Therefore, to prevent germs from infecting more people ...
The means by which an organism transfers from one carrier to another by either direct transmission. (direct contact between infectious host and susceptible host) ...
Start studying Chain of Infection. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Diagram: The chain of infection »é¨Õ£q 3 - 2 Modes of Escape Breaking the Link Respiratory Tract. Microorganisms leave the body of the infected person by means of droplets exhaled as a spray when coughing, sneezing, talking, singing or just breathing. Microorganisms also escape through nose
Chart and Diagram Slides for PowerPoint - Beautifully designed chart and diagram s for PowerPoint with visually stunning graphics and animation effects. Our new CrystalGraphics Chart and Diagram Slides for PowerPoint is a collection of over 1000 impressively designed data-driven chart and editable diagram s guaranteed to impress any audience.
Infection Prevention and Control Germs - HSE.ie
Transmission of infection is considered to be a cycle, commonly referred to as ZThe chain of infection [. In order to prevent the transmission of infection it is necessary to break the chain. Infectious agent (Pathogen) This is any micro-organism that causes infection such as MRSA, Clostridium difficile or influenza.
The Chain of Infection. In order for the spread of infectious diseases to take place, the 'chain of infection' must be completed. The First link in the chain is the causative agent. This is the harmful germ or pathogen that can cause infection, illness. and disease. Examples include bacteria and viruses.
Browse 11 chain of infection diagram stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. chain of infection - chain of infection diagram stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. coronavirus covid-19 impact on global economy and supply chain, financial crisis concept - chain of infection diagram ...
Chain of Infection Alessandra Lerma Influenza Infectious Agent 1 The infectious agent in this case would be the flu. In order to break the chain at this point, one needs to diagnose and treat the individual for the virus. Reservoir 2 The reservoir would be humans. In order to Mode
Chain of Infection In order to control or prevent infection it is essential to understand that transmission of a pathogen resulting in colonisation or infection requires the following 5 vital links: Agent Source Mode of transmission Portal of entry into the host Susceptible host. Agent Types of potential pathogens include: i. Bacteria ii. Viruses
The 6 links in the chain of infection. 1. The pathogen. The first link in the chain of infection is the infectious agent or pathogen which can take the form of: Viruses - such as Influenza A, shingles and Hepatitis. Bacteria - including Lyme disease and Leptospirosis. Fungi - for example Candidiasis and Aspergillosis.




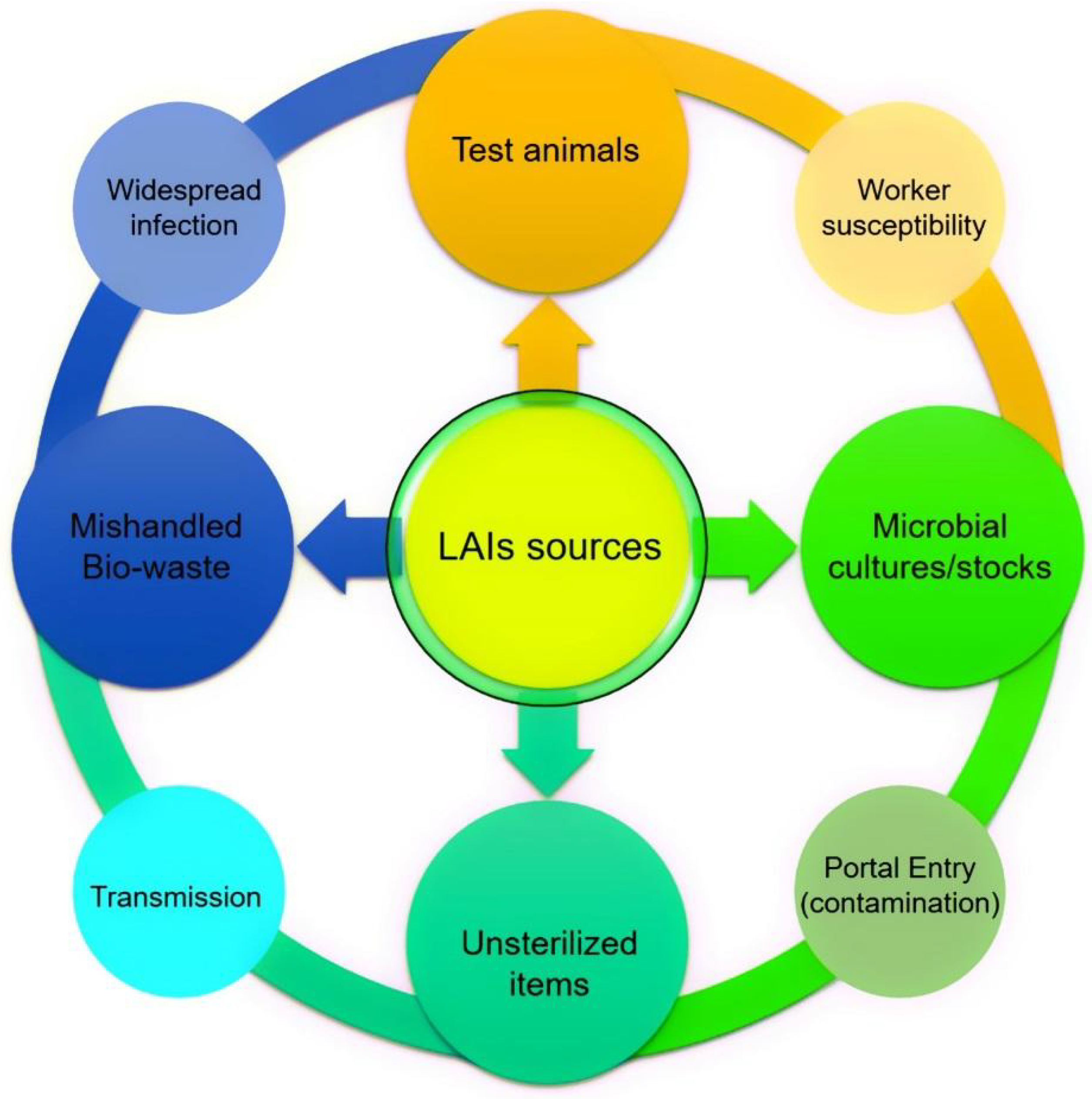


















Comments
Post a Comment