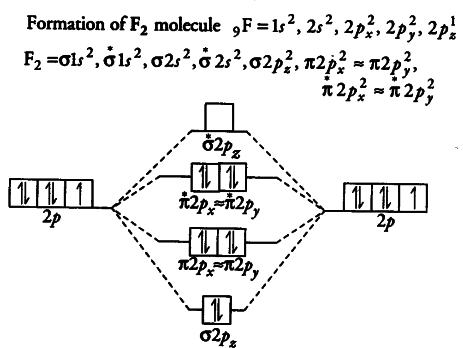
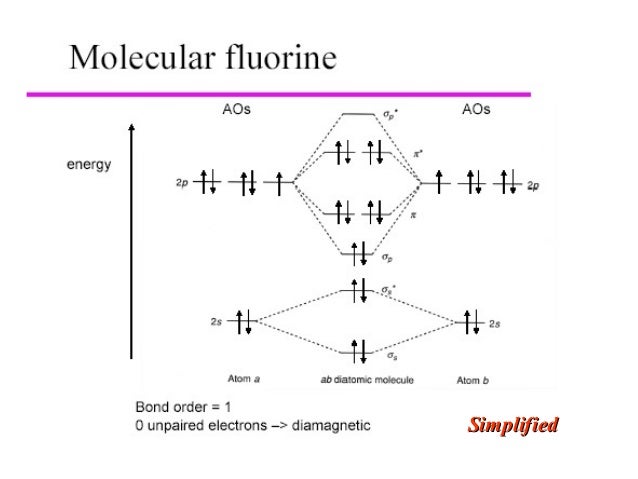
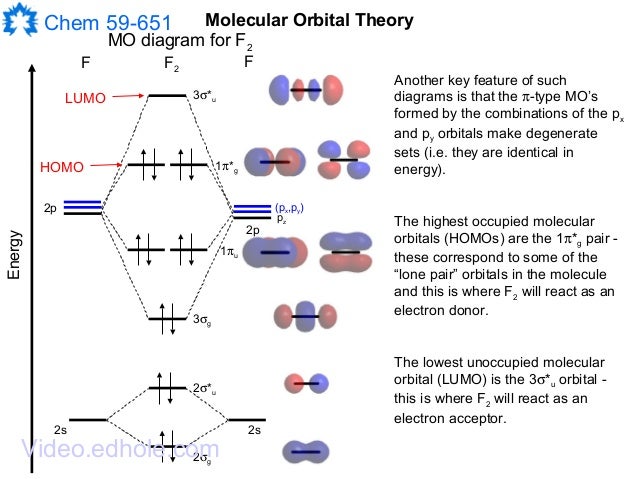
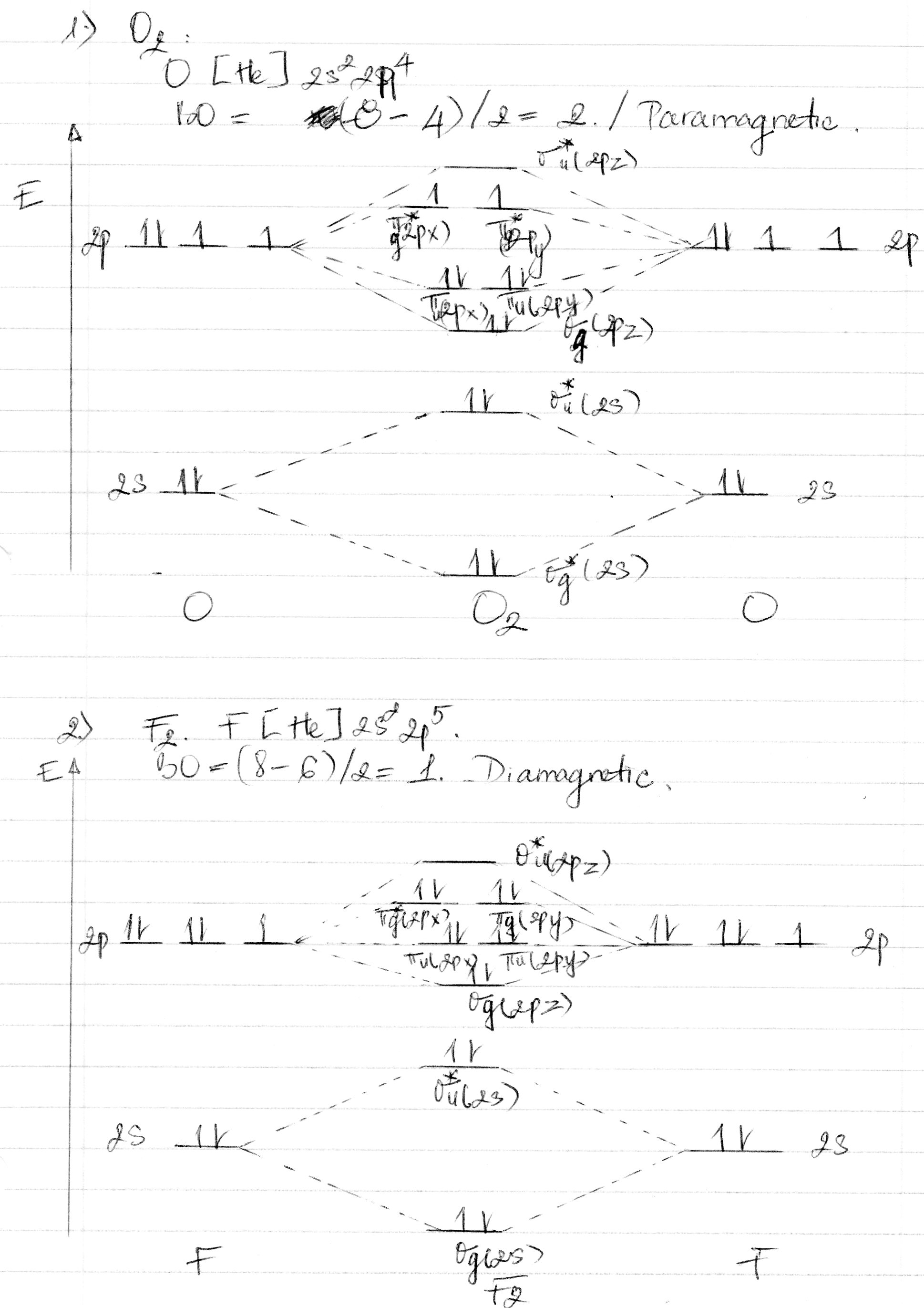
43 molecular orbital diagram f2
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2 Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. May 25, By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal 9 . It is paramagnetic in nature. 6)Li2. Molecular orbital energy level of Li2.Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2, to F 2 The molecular orbital theory (MO) has been introduced for the diatomic hydrogen molecules.
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in

Molecular orbital diagram f2
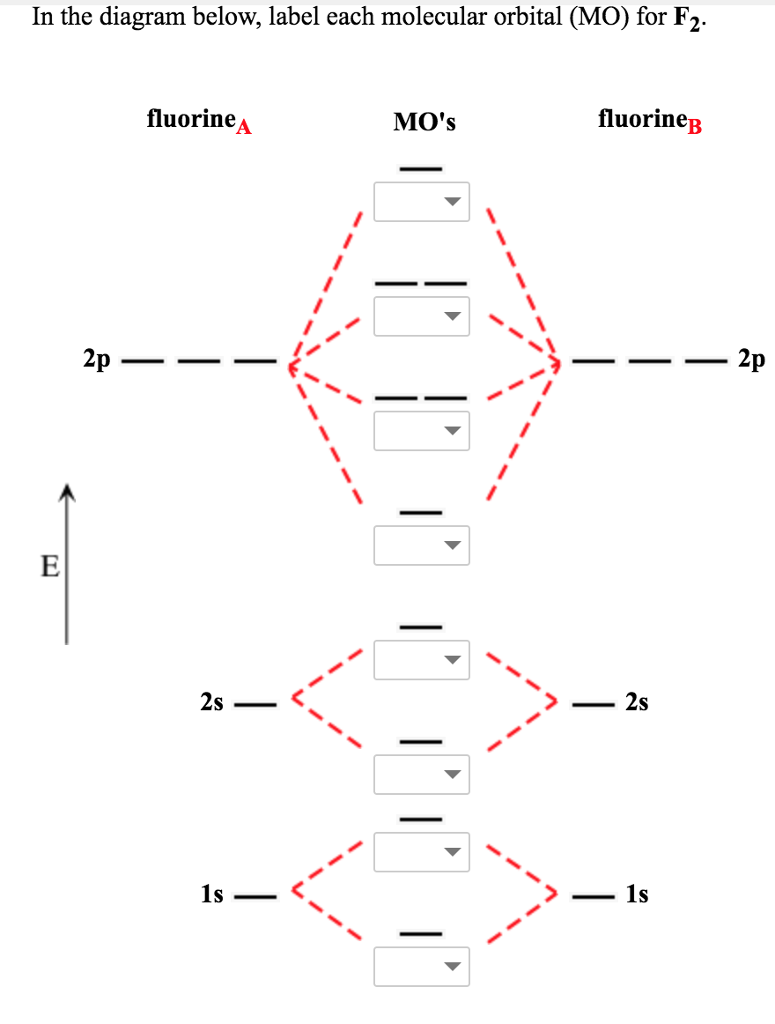
Which statement is true? a. The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. b. When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in energy than the separate atomic orbitals. Below is the molecular orbital diagram for the fluorine molecule (F2) and images of several molecular orbitals that exist in this molecule. Fill the blanks below. Fatom F Fatom А ** tttt pfltit >pft t11 to f1 f1 att с D E F .t1 s stt 24 TL 1. a. The bond order for the F2 molecule is (enter a numeral). b. Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 – Analysis The Magnetically Induced Current Density Molecules molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule
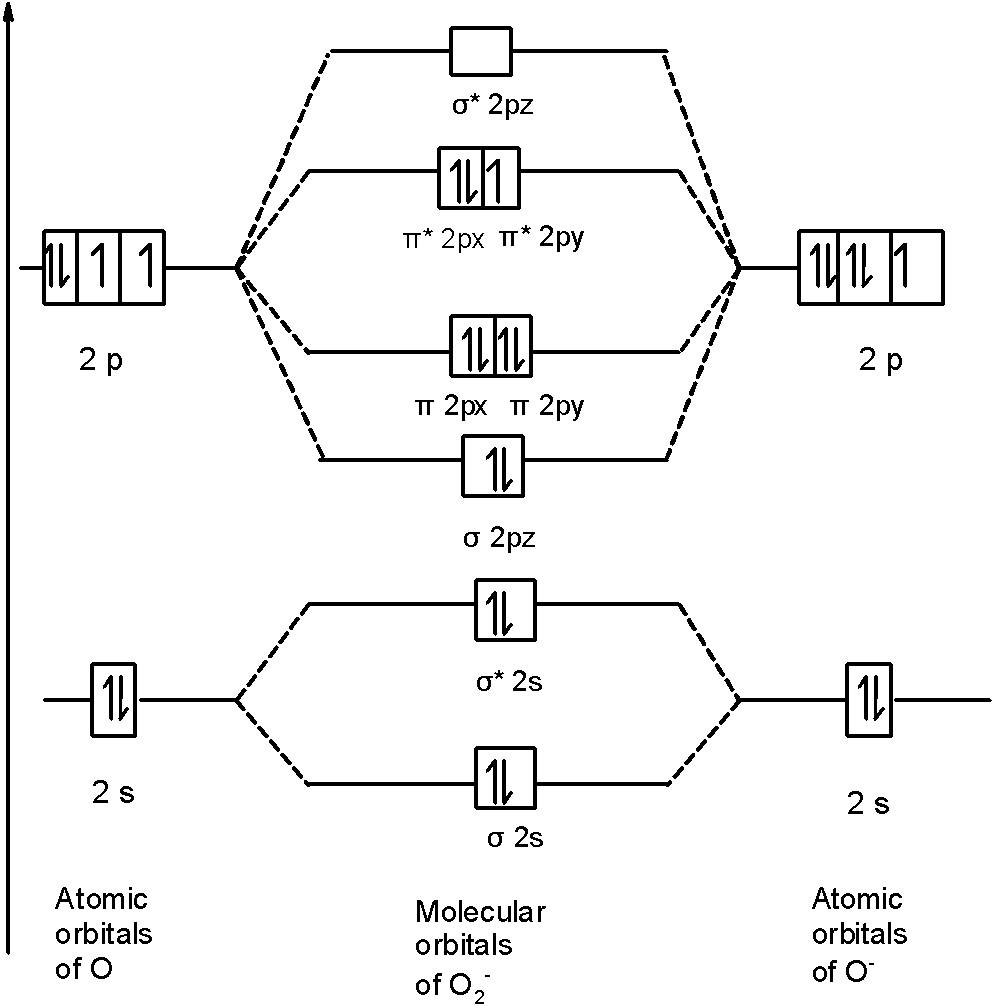
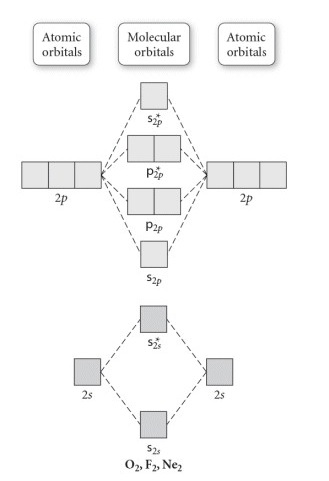
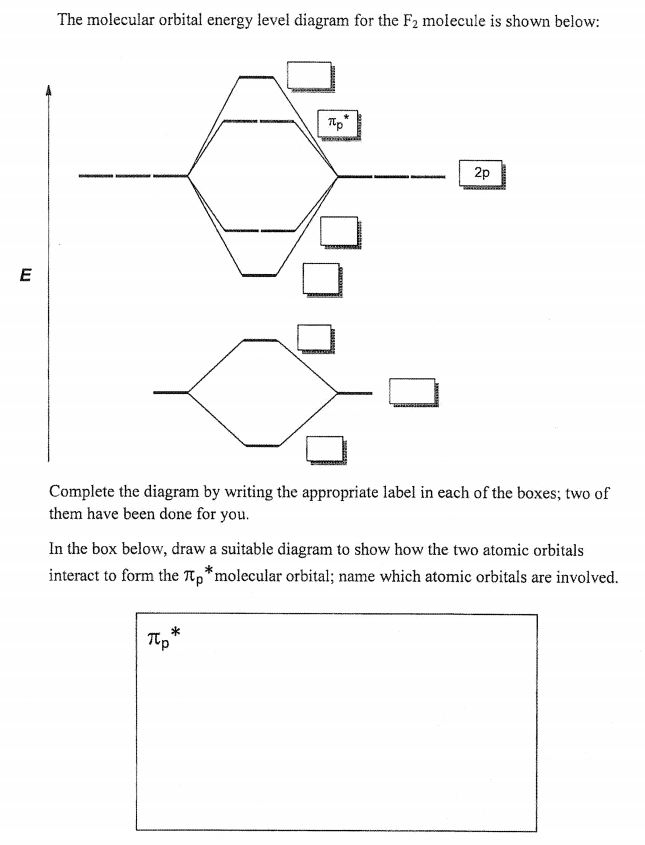
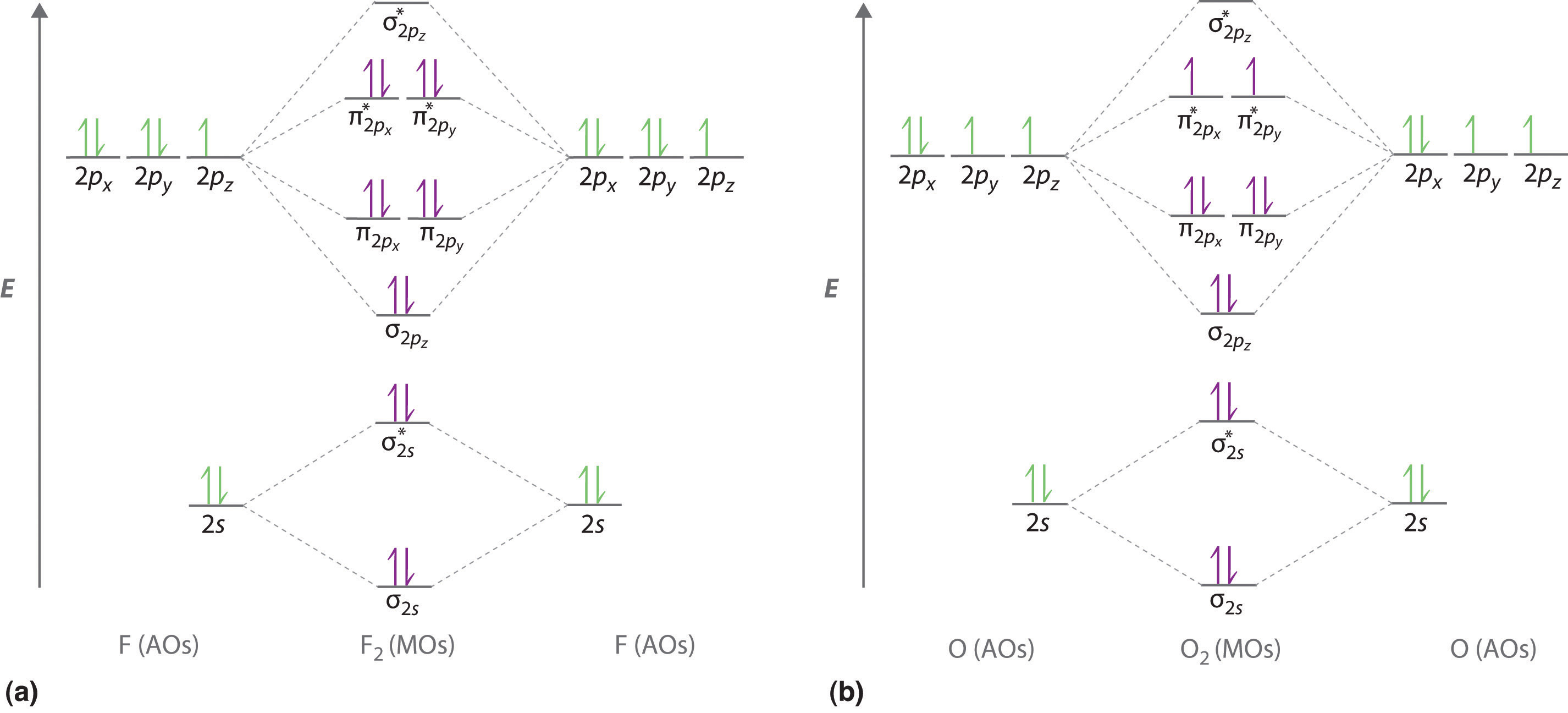
Molecular orbital diagram f2. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below. The case of F2 is a simple one because of the symmetry and diatomicity of the molecule. In more complex molecules (polyatomic and asymmetric), the extent of mixing and thus the contribution of individual atomic orbitals to form a particular molecular orbital depends on the relative energy alignment of the atomic orbitals. F2 Polarity A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equilvalent, overlap them. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help F2 F2 Lowest bond energy Highest bond energy The correct ranking cannot be determined.
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2- Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion 1 Order of filling of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic molecules such as CO. Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. When doing molecular orbitals, the pi-bonds come before sigma for B2,C2, and N2. For O2,F2, and N2, the sigma bond comes first, then the pi-bonds. Why does this ...6 answers · 60 votes: Here is the solution, %3E * For O2 molecule, %3E * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading. #sigma# molecular orbitals are singly-degenerate, and #pi# molecular orbitals are doubly-degenerate. #sigma# molecular orbitals, in principle, get more stabilized upon overlap than #pi# molecular orbitals do. For example, an #ns//ns# overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this:
Molecular orbitals: Orbitals that span two or more atoms. These are constructed by overlapping atomic orbitals (AOs) which match in symmetry and size. In principle, To construct MO diagram of a any Molecule, first, set up Schrödinger wave equation for that molecule and then, solve it!!! A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————... a. F2 20. Refer to the MO Diagrams. Assuming that the molecular orbital energy diagram for a homonuclear diatomic molecule applies to a hero nuclear diatomic molecule, determine bond order for each below. c. NO- d. C2 b. 022- 21 . Which molecule will have the following valence molecular orbital energy level diagram? a*2s2 5 of 5 a. N2 c. 02
A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
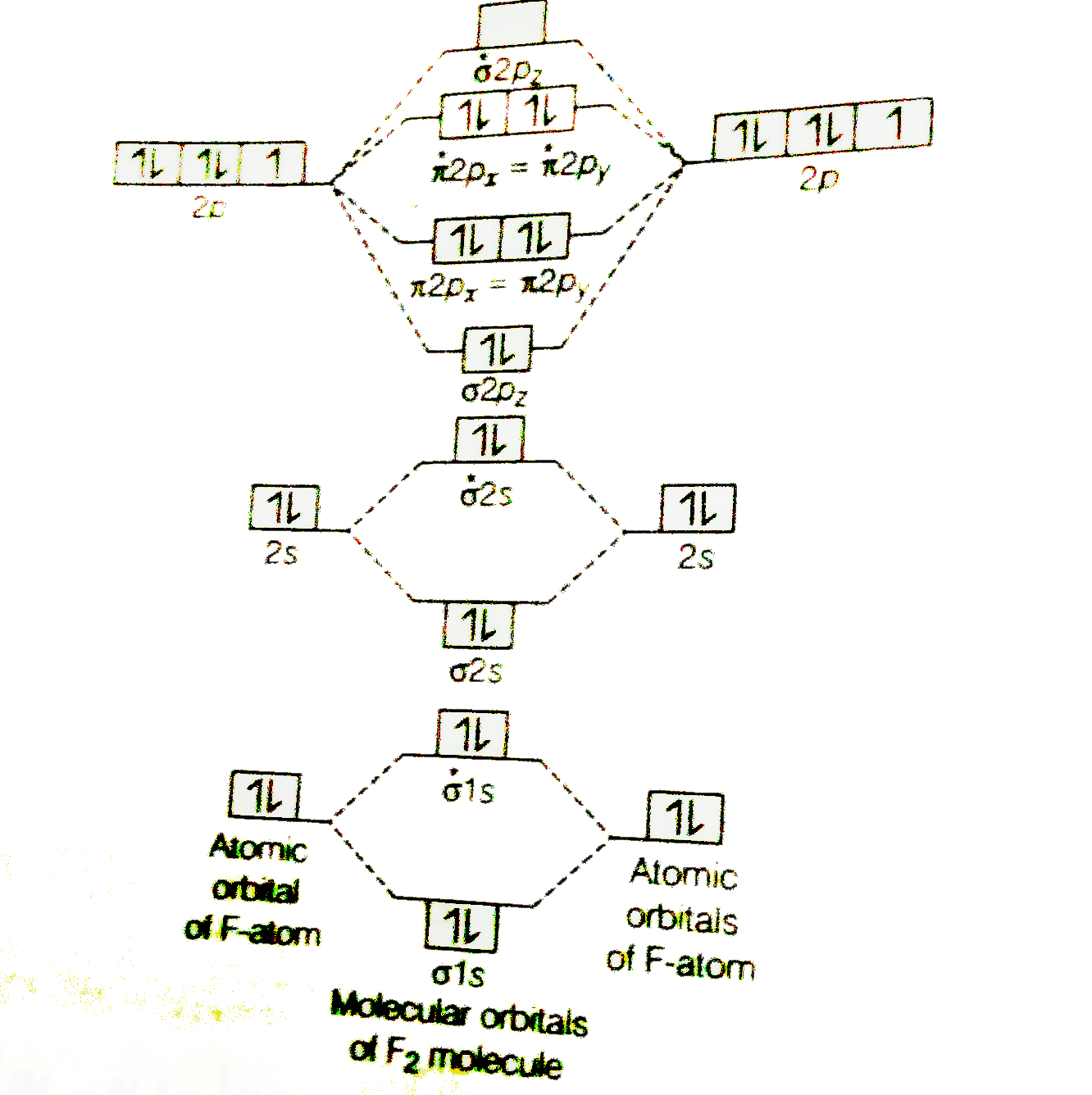
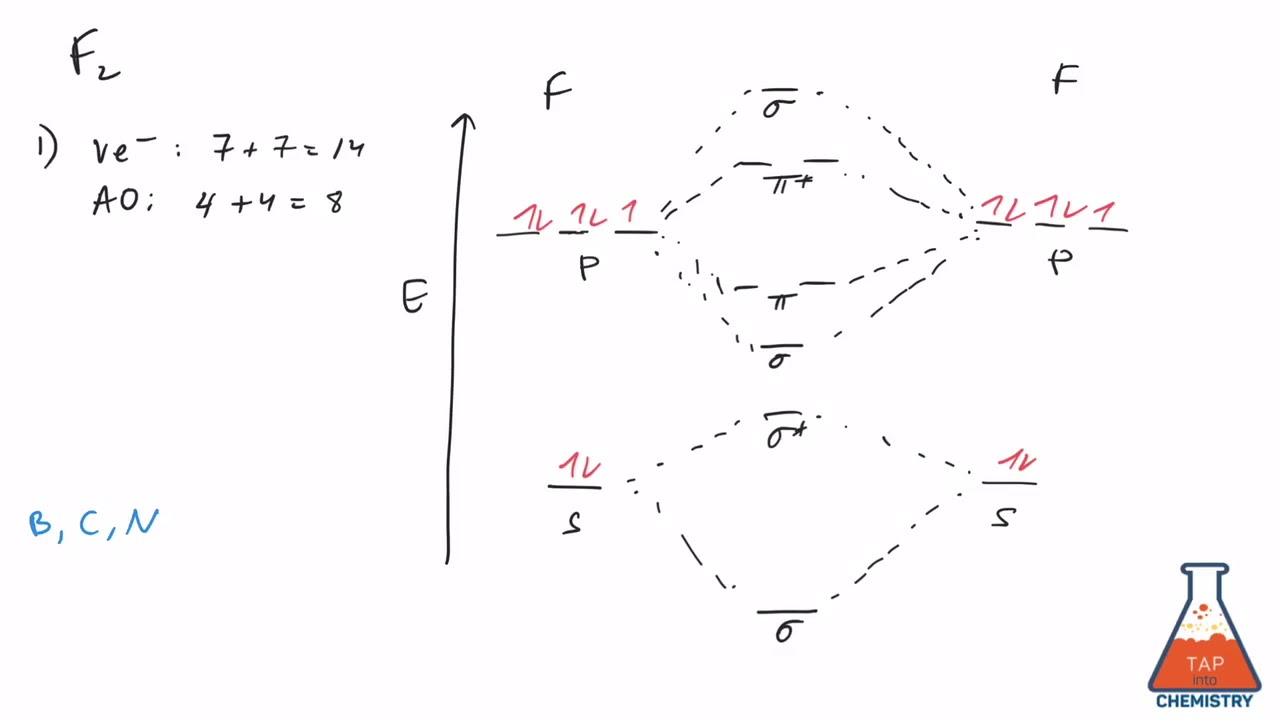
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a. F22+b. Ne22+c. F22-d. O22+e. F2. Recall that the bond order t ells us the strength and length of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is stronger and shorter. a. F22+.
Here is a video that discusses over the Molecular Orbital Diagram for F2+ and F2+. Then compare their bond length, strength, bond order etc. And explaining a...
Formation of Molecular Orbitals. An atomic orbital is an electron wave; the waves of the two atomic orbitals may be in phase or out of phase. Suppose Ψ A and Ψ B represent the amplitude of the electron wave of the atomic orbitals of the two atoms A and B. Case 1: When the two waves are in phase so that they add up and amplitude of the wave is ...
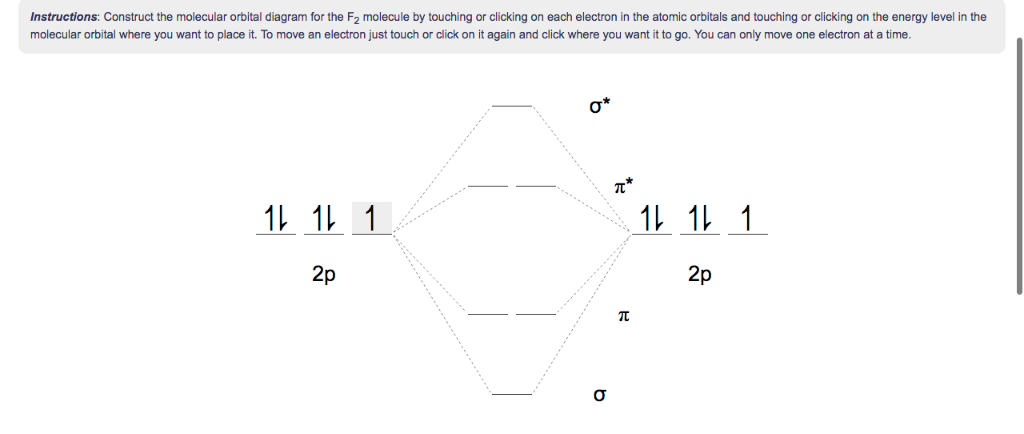
Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-. What type of orbital contains the highest energy electron (s) in F2? pi, antibonding sigma, bonding sigma, antibonding pi, bonding Which atom is larger in size (radius), Cr or Cr3+? Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-.
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following:
Answer (1 of 5): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...
Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule. Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of $ {N_2}$ . Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means. As we know the electron has an electron magnetic dipole moment, which is generally generated by the electron's spin ...
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
Nov 01, 2021 · When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
place the following molecular orbitals in order of decreasing energy for species of O2, F2, and Ne2. start with the highest energy molecular orbital at the top of the list. 1.) o*2p 2.) pie*2p
Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 – Analysis The Magnetically Induced Current Density Molecules molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule
Below is the molecular orbital diagram for the fluorine molecule (F2) and images of several molecular orbitals that exist in this molecule. Fill the blanks below. Fatom F Fatom А ** tttt pfltit >pft t11 to f1 f1 att с D E F .t1 s stt 24 TL 1. a. The bond order for the F2 molecule is (enter a numeral). b.
Which statement is true? a. The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. b. When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in energy than the separate atomic orbitals.
Brain Cancer Chromosomes. Chromosomes prepared from a malignant glioblastoma visualized by spectral karyotyping (SKY) reveal an enormous degree of chromosomal instability -- a hallmark of cancer. Created by Thomas Ried, 2014














Comments
Post a Comment