38 hf orbital diagram
Hartree-Fock self-consistent-field (HF SCF) usually converges fairly well with a good initial guess Stretched bonds, diradicals, transition metals, high-spin states, etc., can cause problems for convergence In high-symmetry cases, the program can guess the wrong orbital occupations, and then have trouble recovering from this Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
The valence bond theory works well to explain the bonding in HF as well, with the 2p orbital of fluorine atom involved in the overlapping. The fluorine atom has the valence electron configuration of 2s 2 2p 5 as shown in the orbital diagram. Figure 1.6d Orbital diagram of valence electrons in fluorine atom
Hf orbital diagram
HF HOMO Orbital. The HOMO orbital is the highest energy molecular orbital occupied by electrons. In HF, the HOMO orbitals are the double degenerate pi 2px and 2py and pi orbitals. To get a 3-D model you can manipulate, click here. Download time may be significant the first time the applet is loaded. It is said that the 1s orbital of hydrogen overlaps and fuses with the 2p orbital of fluorine in a molecule of HF. According to Molecular Orbital Theory, the 2s orbital of F is non-bonding, and the 2pz orbital of F combines with 1s of H. HF Polarity. Polarity is yet another important topic of chemistry that we are going to discuss in this article. Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...
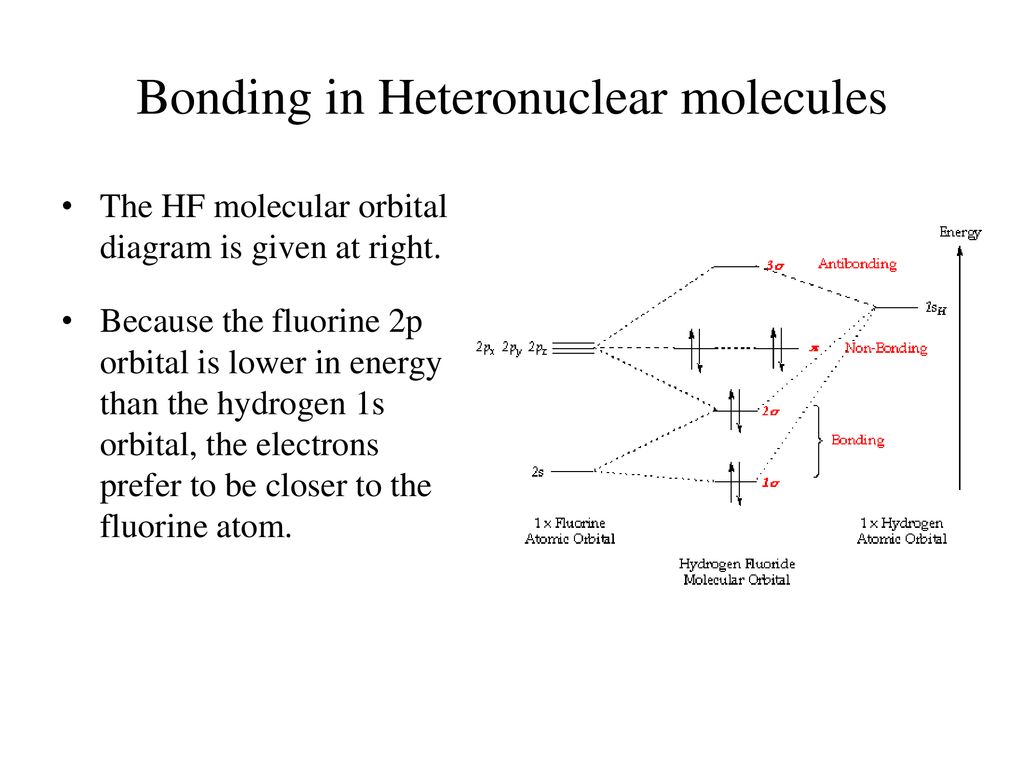
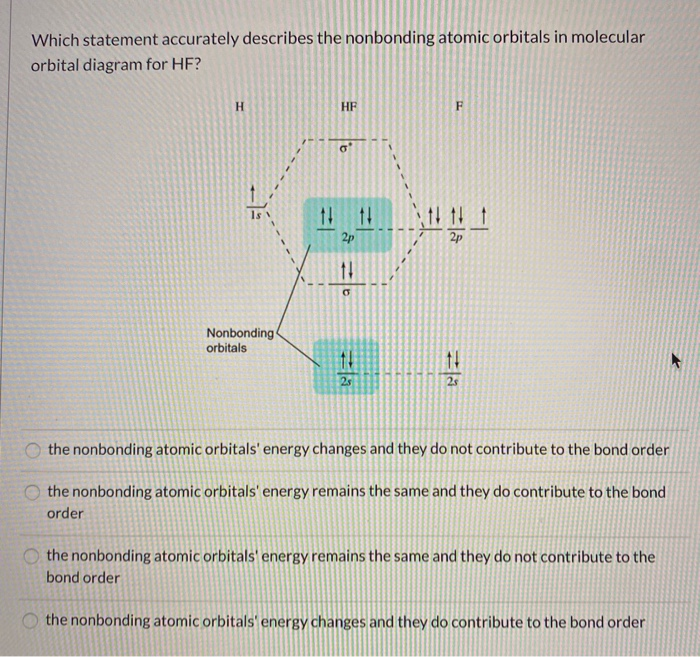
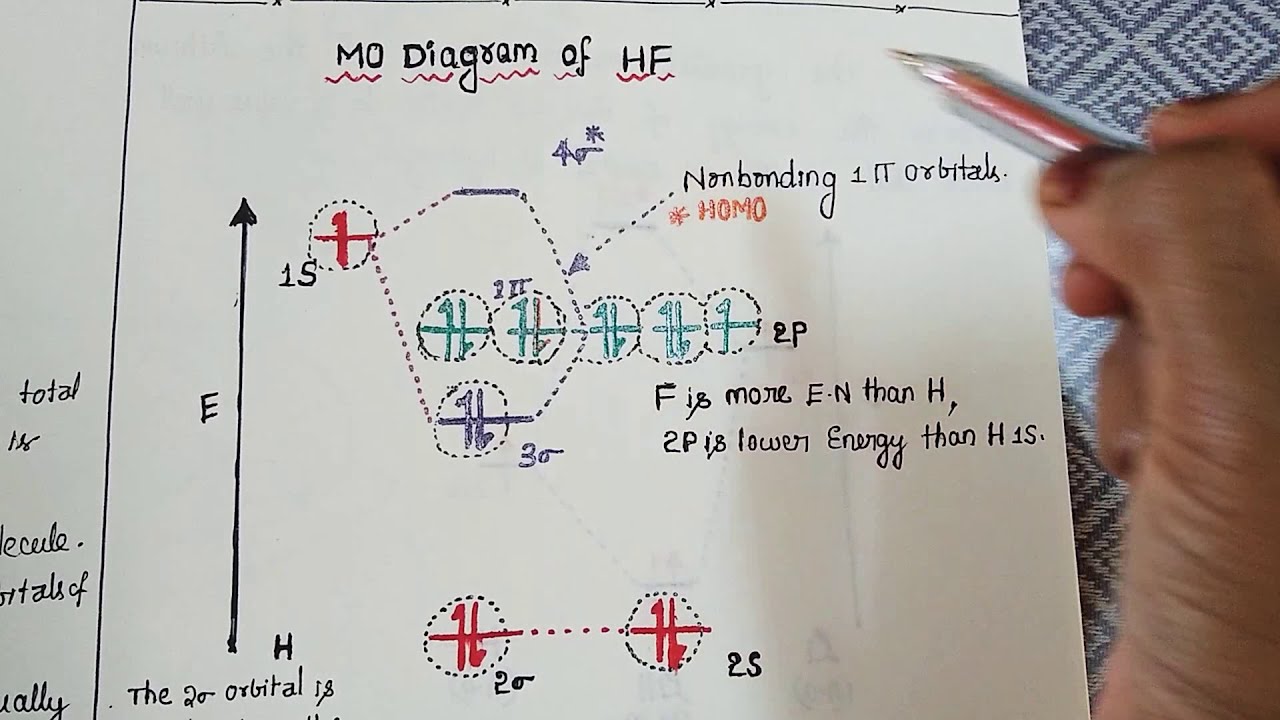
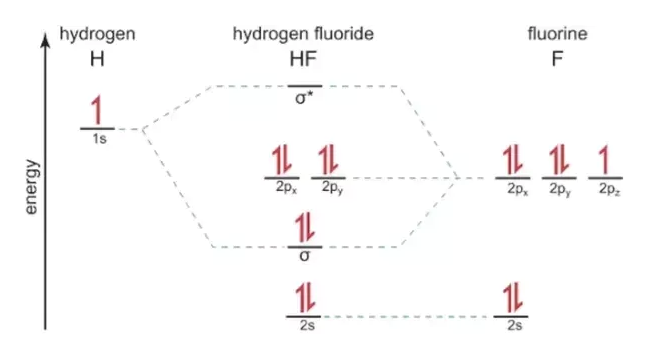
Hf orbital diagram. HF Molecular Orbital Diagram. Hydrogen fluoride is another example of a heteronuclear molecule. It is slightly different in that the π orbital is non-bonding, as well as the 2s σ. From the hydrogen, its valence 1s electron interacts with the 2p electrons of fluorine. This molecule is diamagnetic and has a bond order of one. Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. CONTROLS . Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Which is the molecular orbital diagram for HF? The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combine with s orbital. A linear combination of H1s and F2pz orbitals creates a bonding σ orbital and antibonding σ∗ orbital. The remaining F1s, F2s, F2px, and F2py remain non-bonding orbitals for a bond-order of 1 (See Figure 1). Figure 1: LCAO MO Diagram for HF (Author: LeeAnn Sager. Used with permission.)
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface-CO ... An advanced molecular orbital diagram of HF for the inorganic or physical chemistry student. Molecular orbital diagram for the hf molecule interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma bonding and a sigma antibonding molecular orbital as shown below. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of hf molecule will not be symmetrical. F orbital Diagram. 1 4 electron configuration and orbital diagrams orbital diagrams many times it is necessary to see all the quantum numbers in an electron configuration this the purpose of the orbital diagram s p d f orbitals chemistry the orbital names s p d and f describe electron configuration these line groups are called sharp principal diffuse and fundamental the orbital
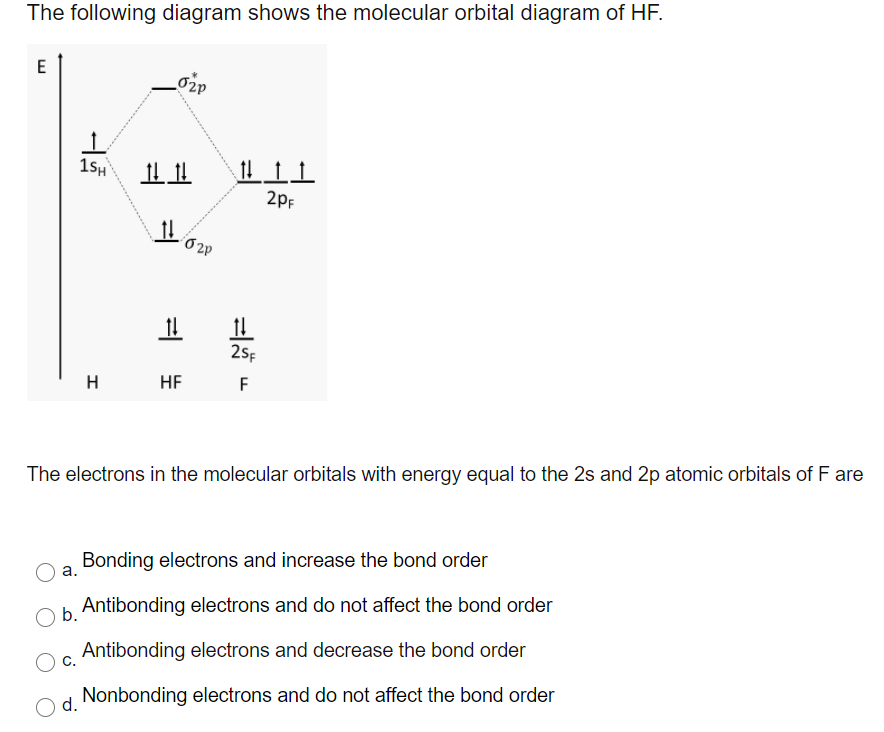
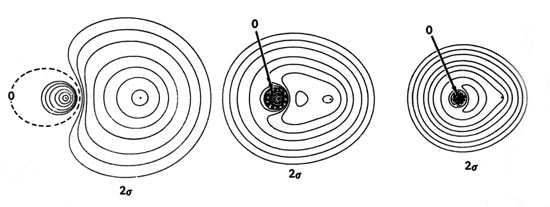
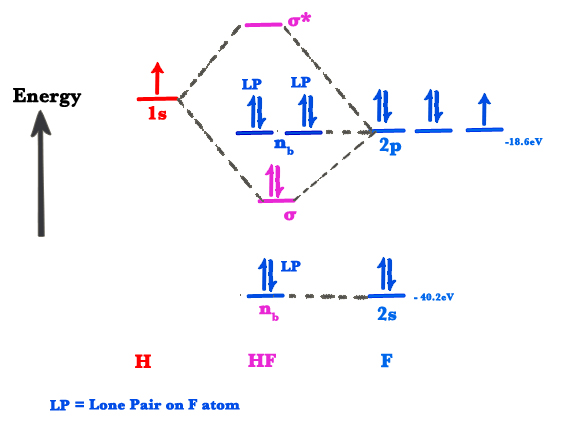
However, in the anti-bonding $4 \sigma^*$ orbital, this polarity is reversed. Caveat: The preceding paragraph may support your intuition and may be right in a few simple cases, but I wouldn't rely on it too heavily. Given below is a diagram showing $2 \sigma$ , $3 \sigma$ and $1 \pi$ MOs in HF Draw the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Hydrogen Fluoride Hydrogen fluoride is an ionic compound that is formed by hydrogen and the most electronegative atom fluorine. Hydrogen fluoride MO diagram. Hydrogen fluoride is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule in which the two atoms are from different periods. In this case, the valence orbital of H is \(1s\) while those of F are \(2s\) and \(2p\). The molecular orbital diagram for HF is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Fluorine (F) Electron Configuration with Full Orbital Diagram. Fluorine electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5. The symbol for fluorine is F. The period of fluorine is 2 and it is a p-block element. The electron configuration of fluorine (F) and the orbital diagram is the main topic of this article.
Hydrogen (H) Electron Configuration with Full Orbital Diagram. Hydrogen electron configuration is 1s 1. Hydrogen is a s-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of hydrogen, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of hydrogen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.
The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
Quantifying The Symmetry Content Of The Electronic Structure Of Molecules Molecular Orbitals And The Wave Function Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C0cp01326a
What is the valence electron of HF? HF is very similar to HF and HCl. Hydrogen has 1 valence electron and Fluorine (in Group 7 with F and Cl) has 7 valence electrons. With the Lewis Structure for HF remember that Hydrogen only needs 2 valence electrons to have a full outer shell. Be sure that you don't use more than the 8 valence electrons ...

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Ne2 And Determine If The Bond Between The Two Atoms Homeworklib
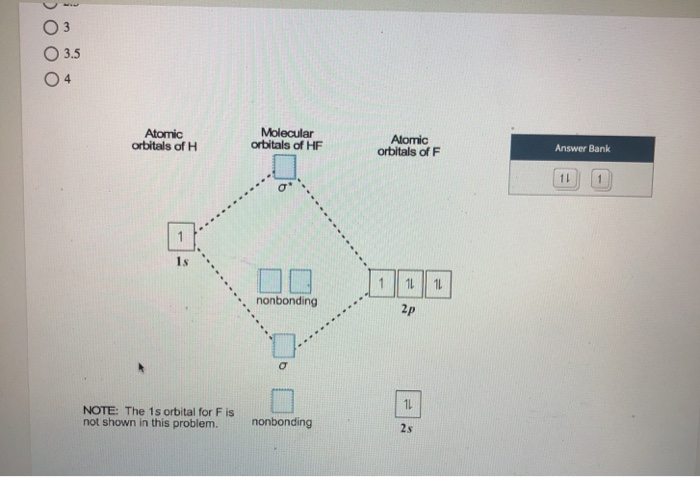
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Use only the valence electrons for your diagram. The 2s orbital of F atom has an energy more than 26 eV lower than that of the H 1s, so there is very little interaction between them. The F 2p orbital (-18.65 eV) and the H 1s (-13.61 eV), on the other hand, have similar energies, allowing them to.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Bonding Orbitals In Methane Sp3 Hybrids . Draw the MO diagram for HBr including energy levels each orbitals shape each orbitals character meaning what atomic orbitals contribute to each MO. Hbr mo diagram. Hydrogen bromide HBr is a colorless gas. Molecular Orbital Theory which is used to sketch the ...

Draw Orbital Diagram Of Fluonine Molecule And Hf Molecule Calculate O N Of Sulphur In So Molecule Brainly In
In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. http://ukcatalogue.oup.com/product/9780199691852.do#...
Orbital diagram of Hafnium (Hf) 73: Orbital diagram of Tantalum (Ta) 74: Orbital diagram of Tungsten (W) 75: Orbital diagram of Rhenium (Re) 76: Orbital diagram of Osmium (Os) 77: Orbital diagram of Iridium (Ir) 78: Orbital diagram of Platinum (Pt) 79: Orbital diagram of Gold (Au) 80:
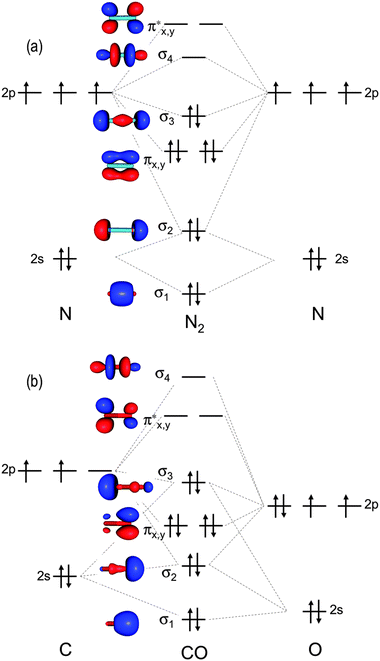
The energy diagram for carbon in CO 2 is shown below. What is the hybridization of oxygen in CO 2. Each oxygen has two lone pairs and forms one s bond and one p bond. This means that there must be three hybridized orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital to make the p bond. This is sp 2 hybridization.
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. 7 Figure 9.44: The electron probability distribution in the bonding molecular orbital of the HF molecule. Note the greater electron density close to the fluorine atom. Figure 9.45: The resonance structures for O3 and NO3-. Note that it is the
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves).
Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...

Oneclass The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Hf Looks Different Than Most Other Diatomic Species Becaus
It is said that the 1s orbital of hydrogen overlaps and fuses with the 2p orbital of fluorine in a molecule of HF. According to Molecular Orbital Theory, the 2s orbital of F is non-bonding, and the 2pz orbital of F combines with 1s of H. HF Polarity. Polarity is yet another important topic of chemistry that we are going to discuss in this article.
HF HOMO Orbital. The HOMO orbital is the highest energy molecular orbital occupied by electrons. In HF, the HOMO orbitals are the double degenerate pi 2px and 2py and pi orbitals. To get a 3-D model you can manipulate, click here. Download time may be significant the first time the applet is loaded.
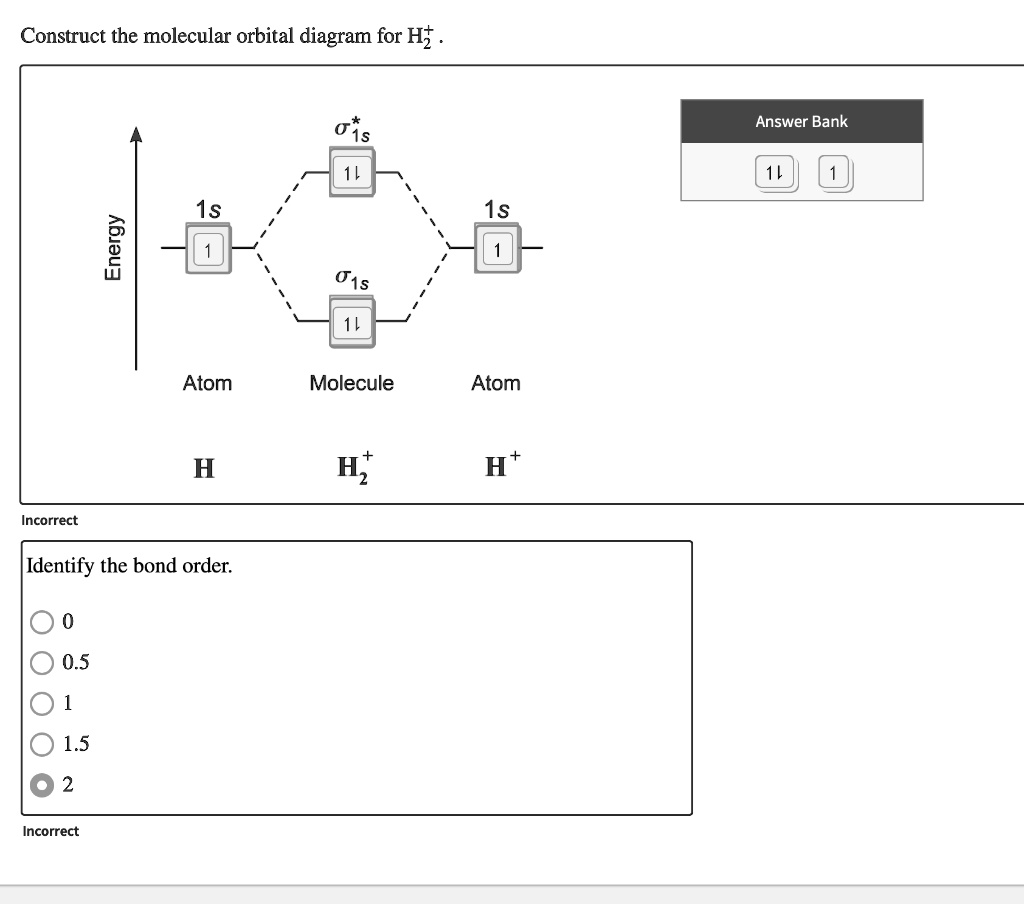
Solved Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Hf Answer Bank Atom Molecule Atom Hz H Incorrect Identify The Bond Order 05 1 5 Incorrect E
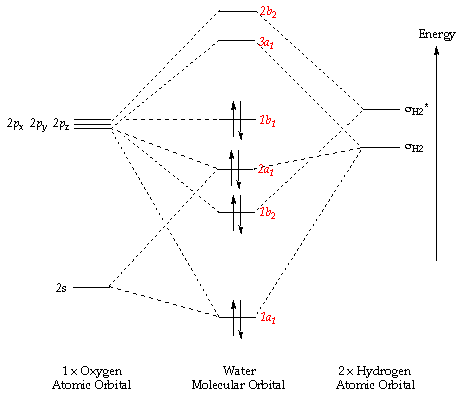














Comments
Post a Comment