38 is lm diagram
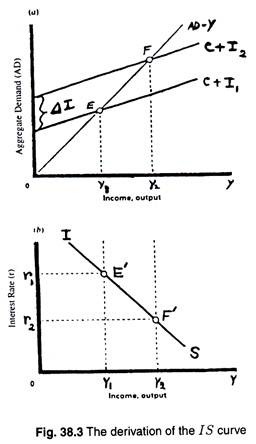
This post goes over the economics and intuition of the IS/LM model and the possible causes for shifts in the two lines. It is possible for the IS curve (Investment and Savings) and the LM curve (Liquidity preference and Money supply) to either increase or decrease based on their determinants. The derivation of IS curve can be made in terms of a four-part diagram. In part (a), we have drawn investment function that shows the inverse relationship ...18 pages
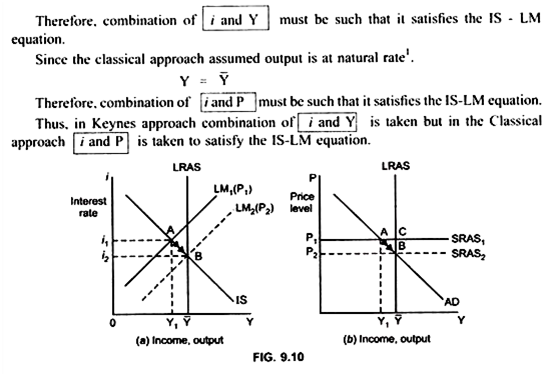
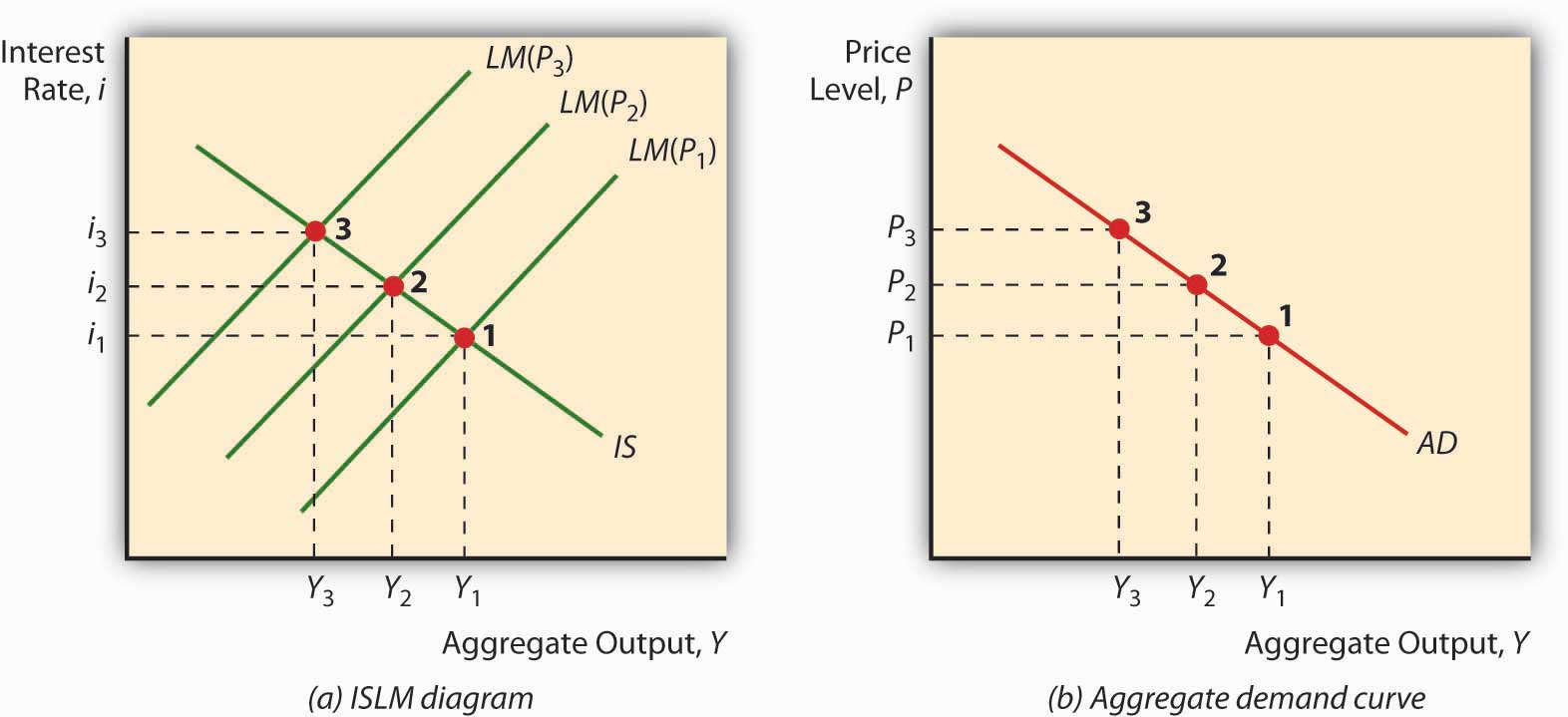
•This is just the IS-LM model but with a more explicit focus on the role played by prices. •We have just shown that a higher price level means an inward shift in the LM curve. •Money and prices have symmetric effects in the model. A doubling of prices has the same impact as a halving of the money supply.

Is lm diagram
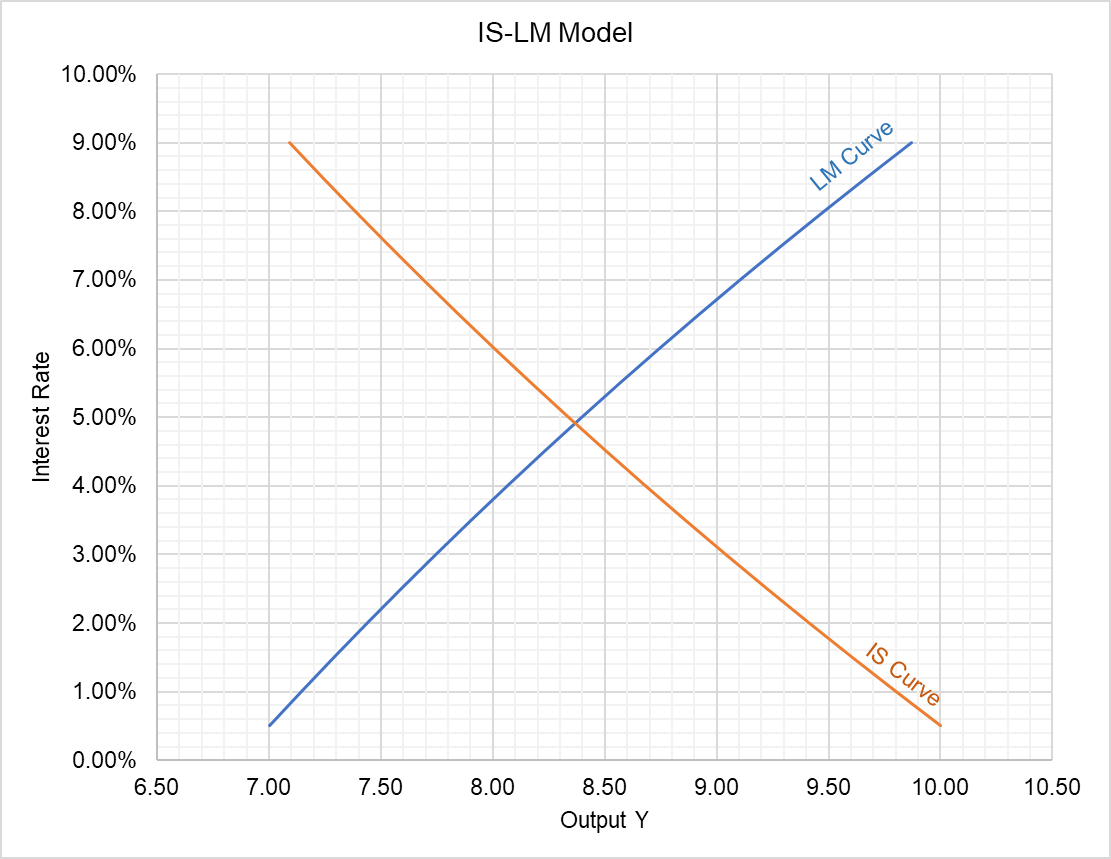
The IS-LM (Investment Savings-Liquidity preference Money supply) model focuses on the equilibrium of the market for goods and services, and the money market.It basically shows the relationship between real output and interest rates.. It was developed by John R. Hicks, based on J. M. Keynes' "General Theory", in which he analysed four markets: goods, labour, credit and money. Draw IS-LM and AD-AS diagrams to show what happened during the 2008-2009 recession (including government's response). 9 Liquidity trap Sometimes policy can lose (part of) its effectiveness. For example, expansionary fiscal policy becomes less effective Axis on the IS-LM diagram. X axis - national income Y axis - interest rate. Link between the money and the goods markets. The rate of interest. The IS curve. Shows an inverse relationship between the interest rate and output - slopes downwards. Slope of the IS curve.
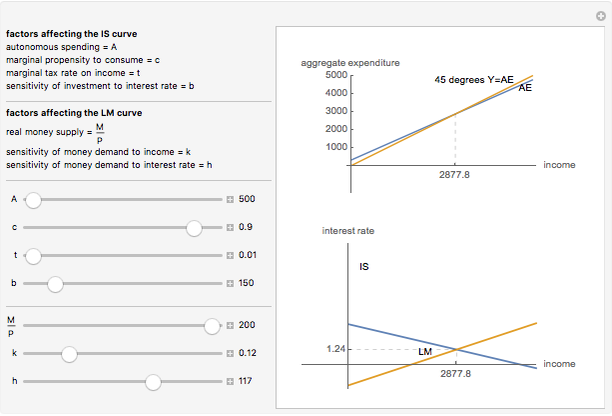
Is lm diagram. Production adjusts to demand to put the economy on the IS curve. Bond prices and the interest rate adjust to achieve equilibrium in financial markets, putting ...3 pages The basis of the IS-LM model is an analysis of the money market and an analysis of the goods market, which together determine the equilibrium levels of interest ... The diagram usually used to analyze the IS-LM model has the nominal interest rate and output, rather than the nominal exchange rate and output, on its axes. Like the DD-AA diagram, the IS-LM diagram determines the short-run equilibrium of the economy as the intersection of two individual market equilibrium curves, called IS and LM. The LM curve summarizes equilibrium in the market for money. It's upward sloping in the diagram. Increases in M shift it to the right and down. [Write down the equation and draw the graph.] Equilibrium in the IS/LM model is represented by the intersection of the IS and LM curves. Increases in G raise Y and r. Increases in M raise Y but lower r.
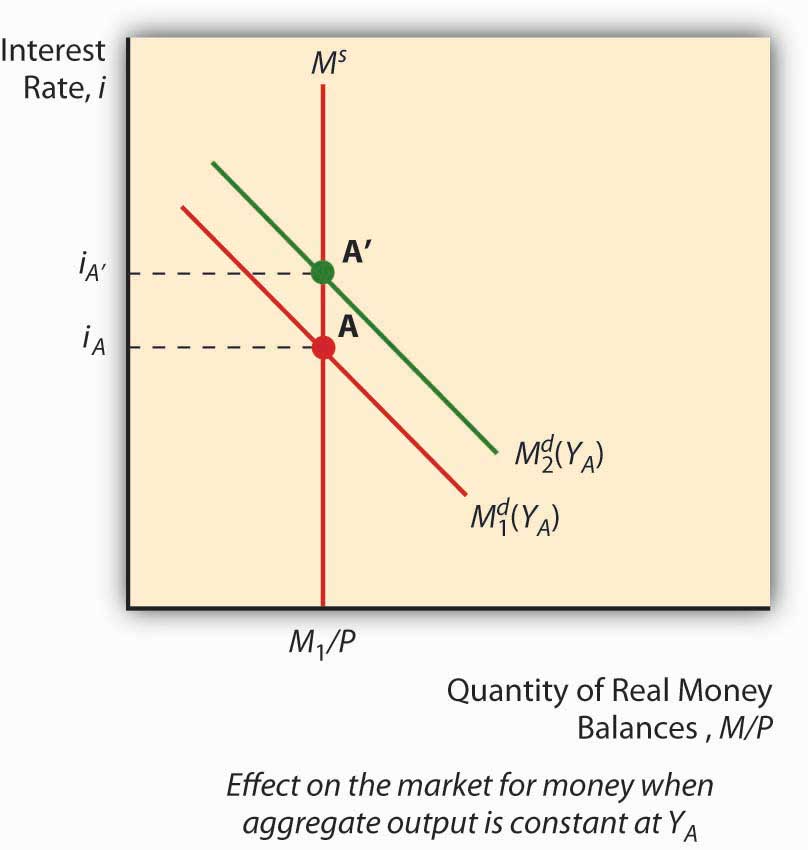
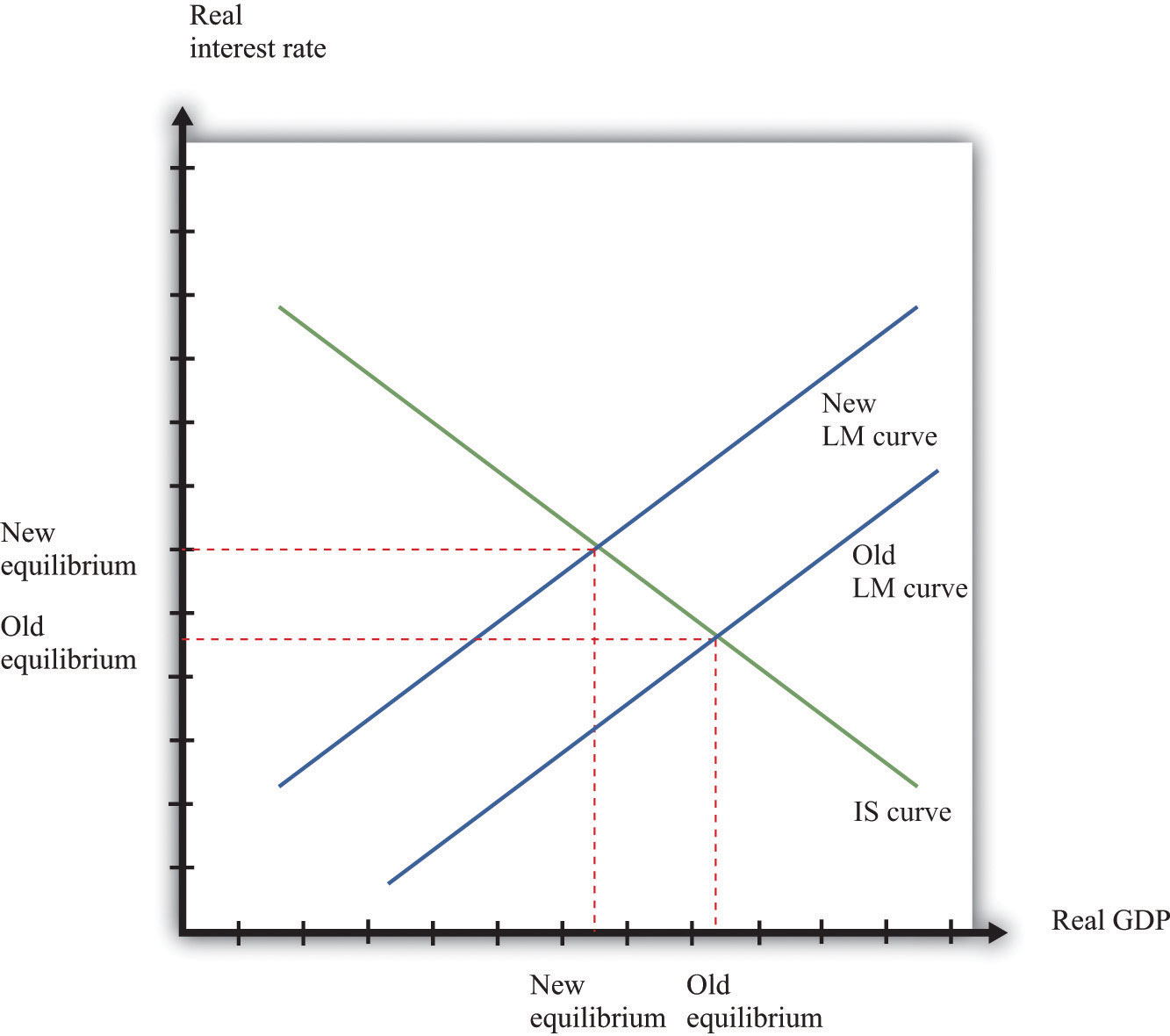
The IS-LM-BP model (also known as IS-LM-BoP or Mundell-Fleming model) is an extension of the IS-LM model, which was formulated by the economists Robert Mundell and Marcus Fleming, who made almost simultaneously an analysis of open economies in the 60s.Basically we could say that the Mundell-Fleming model is a version of the IS-LM model for an open economy. The LM curve. The LM curve shows all combinations of R and Y, where the money market is in equilibrium. The LM-curve slopes upwards. The money market is in equilibrium when Md(Y, R) = Ms.In section 12.3.6 we demonstrated how the money market diagram will determine R when we know Y.In this case, the question to consider is the following: What must happen to R when we change the Y if we want the ... 2.2. The nancial market - Shifts of the LM curve What happens if the nominal money supply increases? Real money supply goes up Demand for money should go up too, to maintain equilibrium: the interest rate must decrease For any level of output, the corresponding level of interest rate is now lower,!downward shift of the LM curve. Understanding Equilibrium in the IS/LM Model 1995 version Prof. Humberto Barreto 1 Introduction: This brief work is designed to provide additional ammunition for the student in the ongoing war against IS/LM confusion and ignorance. The author has claimed in his Notes on Macroeconomic Theory (1995) that,
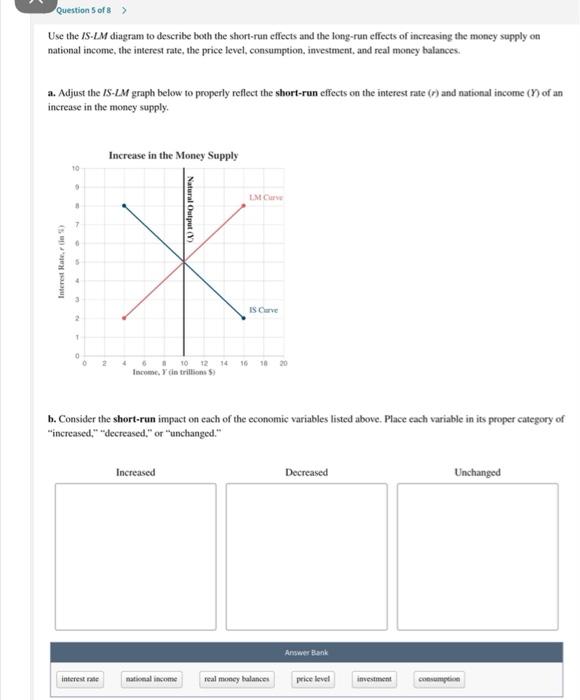
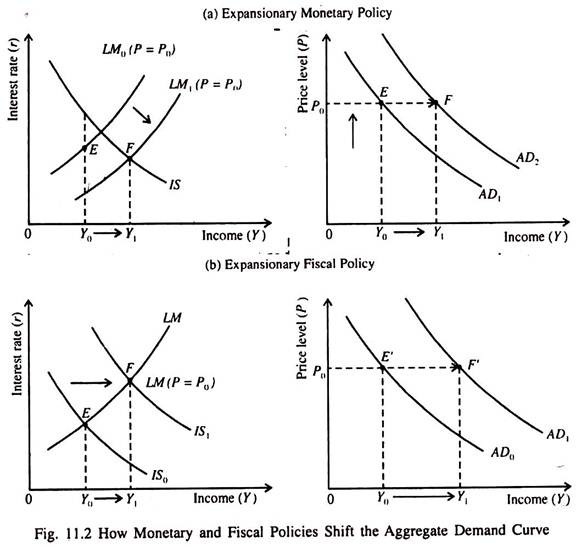
To the right of the LM curve, there is an excess demand for money, inducing people to sell bonds for cash, which drives bond prices down and hence i up to the LM curve. Figure 21.4 IS-LM diagram: equilibrium in the markets for money and goods Fig. 38.6 shows how the LM curve is derived. The right hand diagram [part (b)] shows the money market. The supply of money is the vertical line M, since it is fixed by the Central Bank. The two demand for money curves L 1 and L 2 correspond to two different income levels. Transcribed image text: Aggregate Demand II: Applying the IS-LM Model — End of Chapter Problem Use the IS-LM diagram to describe both the short-run effects and the long-run effects of increasing the money supply on national income, the interest rate, the price level, consumption, investment, and real money balances. a. Adjust the IS-LM graph below to properly reflect the short-run effects on ... The IS-LM model, or Hicks-Hansen model, is a two-dimensional macroeconomic tool that shows the relationship between interest rates and assets market (also known as real output in goods and services market plus money market).The intersection of the "investment-saving" (IS) and "liquidity preference-money supply" (LM) curves models "general equilibrium" where supposed simultaneous ...
shift the LM curve at all. 2) Use the IS-LM diagram to describe the short-run and long-run effects of the following changes on national income, the interest rate, the price level, consumption, investment, and real money balances. a) An increase in the money supply.
ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make an in-depth study of the IS-LM Curve Model. After reading this article to learn about: 1. Structure of the IS-LM Model 2. The Basic IS-LM Curve Model 2. Usefulness 3. Limitation. Structure of the IS-LM Model: The IS-LM curve model emphasises the interaction between the goods and assets markets. The Keynesian […]
a) Draw three diagrams with an IS - LM diagram on the top left, a domestic return - foreign return diagram on the right, and a money market diagram on bottom left. Begin at point A and let the cent...
The IS-LM Model Due Mar 18 1. Fun with the Keynesian Cross: a. Use the geometry of the Keynesian Cross diagram shown at the right to derive that the government purchases multiplier is 1/(1-MPC), where MPC is the slope of the planned expenditure line, E. In the figure, planned expenditure has increased (for any given income) by the amount of an
Example: IS-LM diagram. This figure shows how an economy utilizing fixed exchange rates will react according to the IS-LM curve (sometimes also known as Mundell Flemming) Do you have a question regarding this example, TikZ or LaTeX in general? Just ask in the LaTeX Forum. Oder frag auf Deutsch auf TeXwelt.de.
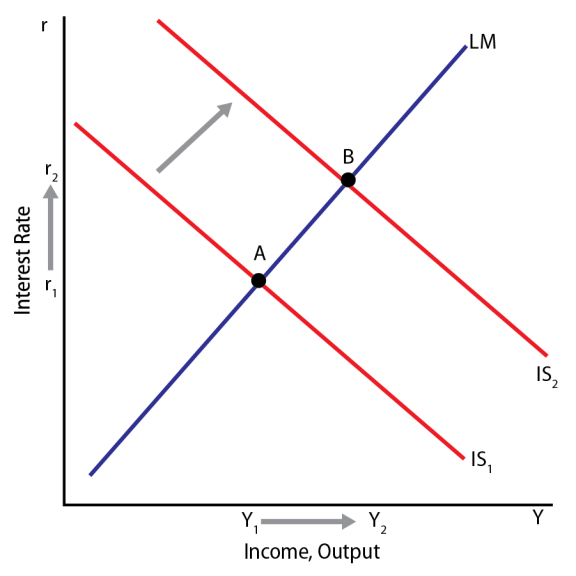
But with the LM curve, we know the new equilibrium point has a higher output than the original equilibrium but the increase in output is less than the horizontal shift of the IS curve (use IS-LM diagram or the argument we presented in class - higher income leads to higher demand for money which raises interest rate.

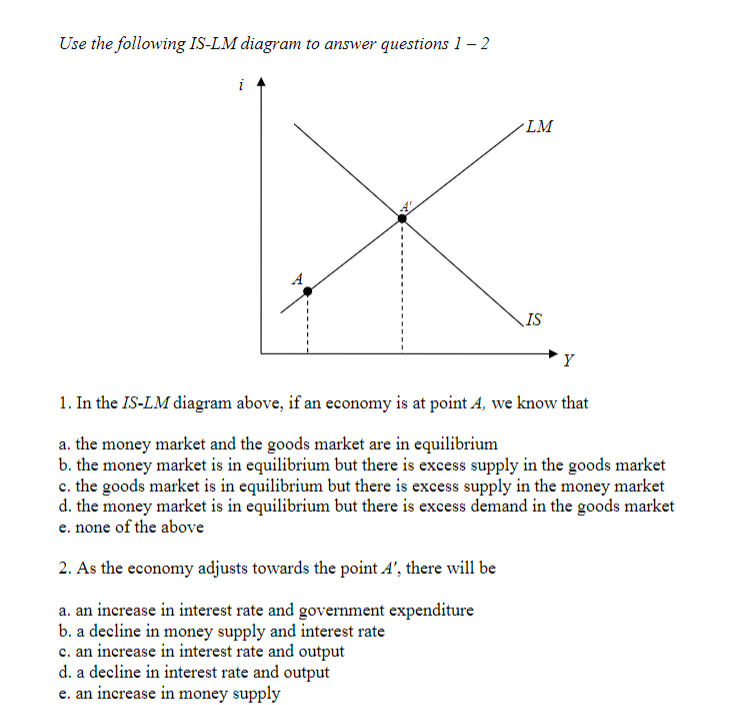
Answer True Or False Use An Is Lm Diagram To Explain Your Answer Money Demand Shocks Will Not Affect The Output Level So Long As The Fed Pegs Interest Rates Study Com
The IS-LM model is a way to explain and distill the economic ideas put forth by John Maynard Keynes in the 1930s. The model was developed by the economist John Hicks in 1937, after Keynes published his magnum opus The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936).The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936).
We now need to present both stock (asset market) and flow (commodity market) equilibrium on the same graph. The conventional way to do this is to put the real ...
Live. •. Also known as the Hicks-Hansen model, the IS-LM curve is a macroeconomic tool used to show how interest rates and real economic output relate. IS refers to Investment-Saving while LM refers to Liquidity preference-Money supply. These curves are used to model the general equilibrium and have been given two equivalent interpretations.
Solved Use The Is Lm Diagram To Describe The Short Run And Long Run Effects Of The Following Changes On National Income The Interest Rate The Pri Course Hero
The diagram below shows the determination of Y, R and L in the IS-LM model. Fig. 12.6: Determination of Y, R and L of the IS-LM model. We start at top to the left and extend Y * down, through the "mirror" at the bottom left, on to the production function at the bottom right and then up to the diagram representing the labor market.
The IS-LM model, which stands for "investment-savings" (IS) and "liquidity preference-money supply" (LM) is a Keynesian macroeconomic model that shows how the market for economic goods (IS ...
Explanation: Equilibrium is at the intersection of IS and LM.With a pegged exchange rate this may lie off the BP curve, indicating a BOP in surplus (+) above or deficit (-) below.With a floating exchange rate, a secondary adjustment of the exchange rate, E, (with effects shown in green) must move the three curves so as to intersect in one place, in order to get equilibrium in the exchange market.

Use The Is Lm Diagram To Illustrate And Give An Intuitive Explanation Of The Relationship Between The Effectiveness Of Monetary Policy And The Responsiveness Of Investment To The Interest Rate Frac Dl Dj On The
The IS-LM Curve Model (Explained With Diagram)! The Goods Market and Money Market: Links between Them: The Keynes in his analysis of national income explains that national income is determined at the level where aggregate demand (i.e., aggregate expenditure) for consumption and investment goods (C +1) equals aggregate output.

Use The Is Lm Diagram To Illustrate And Give An Intuitive Explanation Of The Relationship Between The Effectiveness Of Monetary Policy And The Responsiveness Of Investment To The Interest Rate Frac Dl Dj On The
How a change in fiscal policy shifts the IS curve. Created by Sal Khan. IS-LM. Investment and real interest rates. Connecting the keynesian cross to the IS curve. Loanable funds interpretation of IS curve. LM part of the IS-LM model. Government spending and the IS-LM model. This is the currently selected item.
The IS LM model is a model used in macroeconomics to help explain the possible relationships between the interest rate and real GDP. While not very accurate for real world analysis, it gives an interesting look at possible outcomes of various policy tools for a classroom setting.
Axis on the IS-LM diagram. X axis - national income Y axis - interest rate. Link between the money and the goods markets. The rate of interest. The IS curve. Shows an inverse relationship between the interest rate and output - slopes downwards. Slope of the IS curve.
Draw IS-LM and AD-AS diagrams to show what happened during the 2008-2009 recession (including government's response). 9 Liquidity trap Sometimes policy can lose (part of) its effectiveness. For example, expansionary fiscal policy becomes less effective
The IS-LM (Investment Savings-Liquidity preference Money supply) model focuses on the equilibrium of the market for goods and services, and the money market.It basically shows the relationship between real output and interest rates.. It was developed by John R. Hicks, based on J. M. Keynes' "General Theory", in which he analysed four markets: goods, labour, credit and money.










Comments
Post a Comment