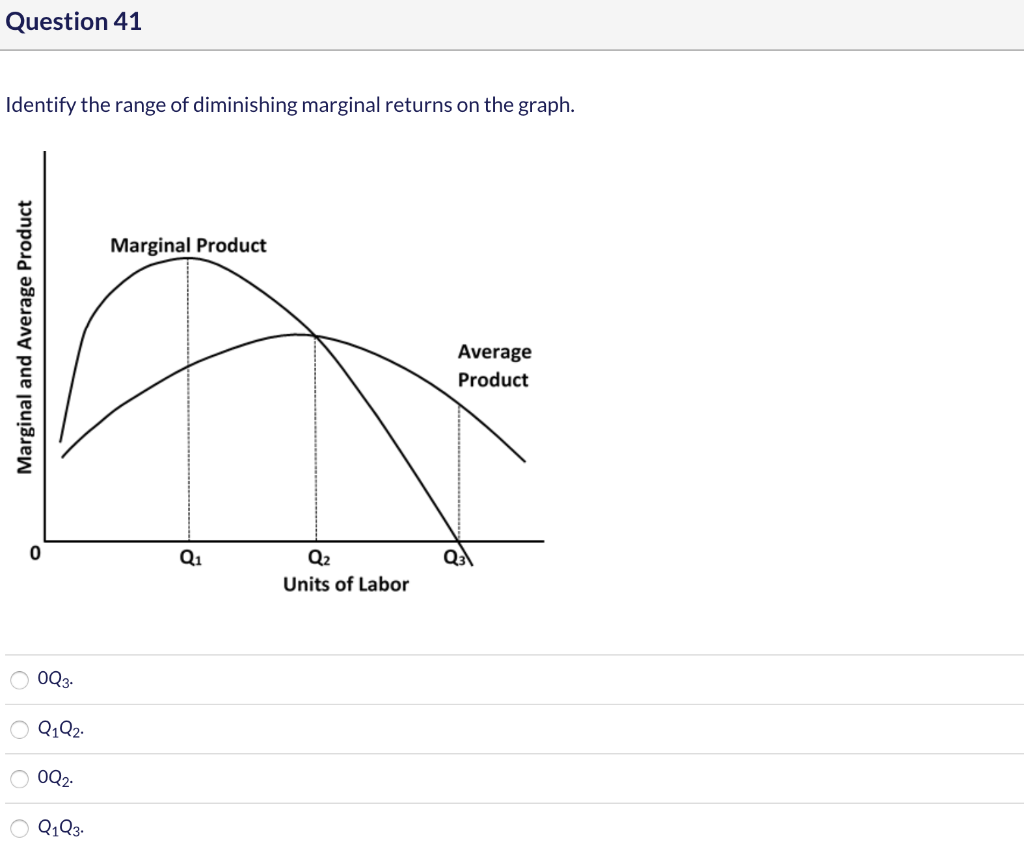
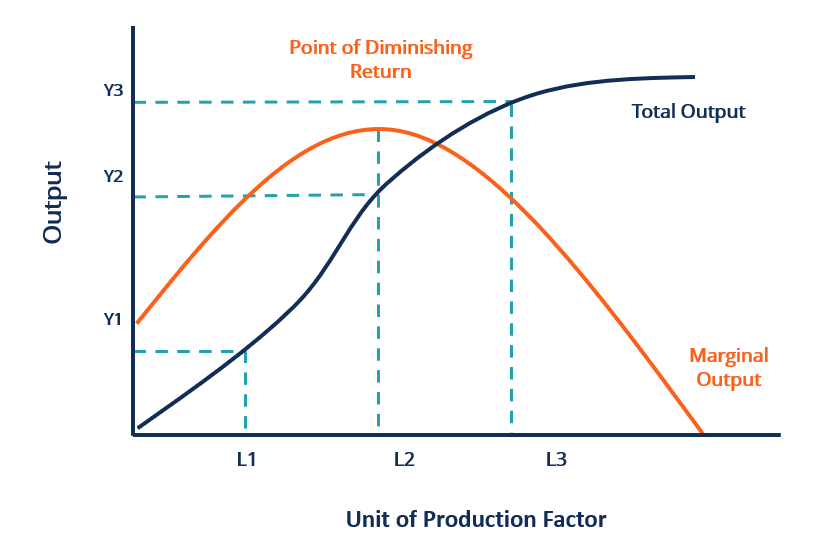
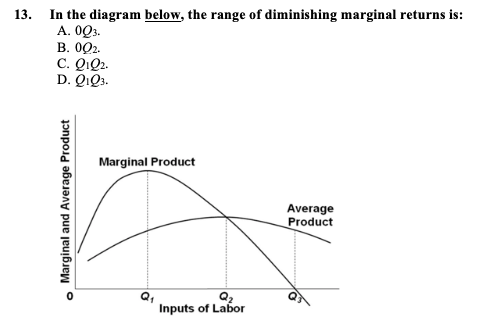
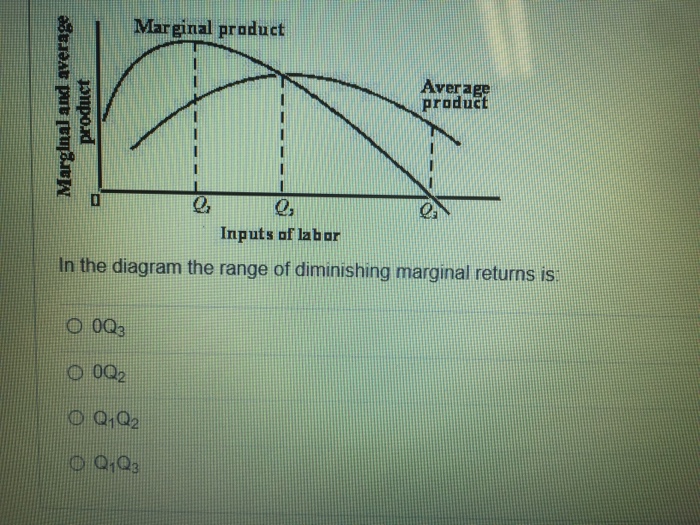
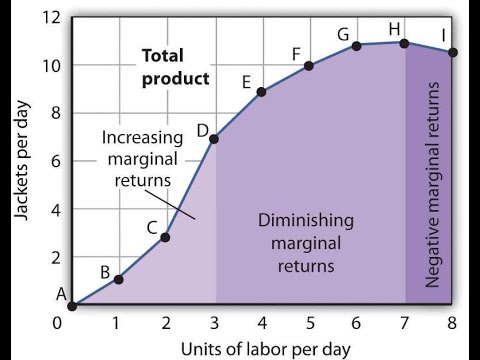
42 in the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is
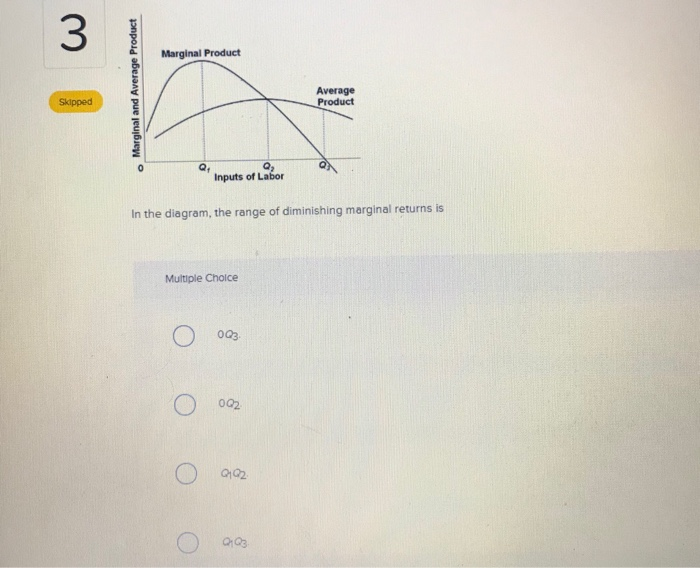
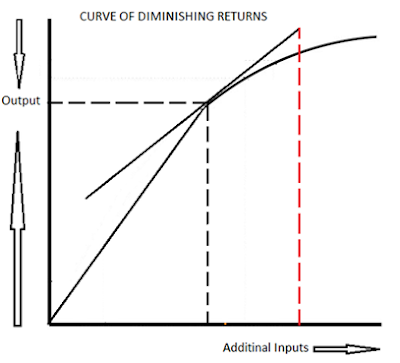
(a) See the graph. Over the 0 to 4 range of output, the TVC and TC curves slope upward at a decreasing rate because of increasing marginal returns. The slopes of the curves then increase at an increasing rate as diminishing marginal returns occur.' (b) See the graph. 8. In the diagram above, the range of diminishing marginal returns is A. Q 1 - Q 3. B. 0 - Q1. C. 0 - Q 2. D. Q1- Q2. 9. A mortgage payment due every month for a farm is an example of what type of cost?
In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is: A) 0Q3. B) 0Q2. C) Q1Q2. D) Q1Q3. A: D. Refer to the above data. When total product is increasing at an increasing rate, marginal product is: A) positive and increasing. ... diminishing marginal returns B) an increase in the wage rate C) a decrease in the wage rate D) increasing ...
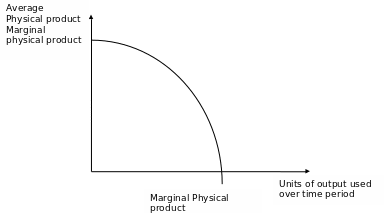
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is
The marginal cost is shown in relation to marginal revenue (MR), the incremental amount of sales revenue that an additional unit of the product or service will bring to the firm. This shape of the marginal cost curve is directly attributable to increasing, then decreasing marginal returns (and the law of diminishing marginal returns). Q (1) Explain and illustrate with diagrams the differences between diminishing marginal returns and decreasing economies of scale and cite causes and examples. Ans. The law of diminishing returns is also called the law of variable proportion, as the proportions of each factor of production employed keep changing as more of one factor is added. MC When the marginal cost (MC) increases, it SRAC Q means the cost of producing one additional unit of the good becomes higher. The MC rises due to diminishing marginal returns. This is because if we are gaining less output from raw materials (factors of production e.g. labour), this means we need more of it to produce the next unit,
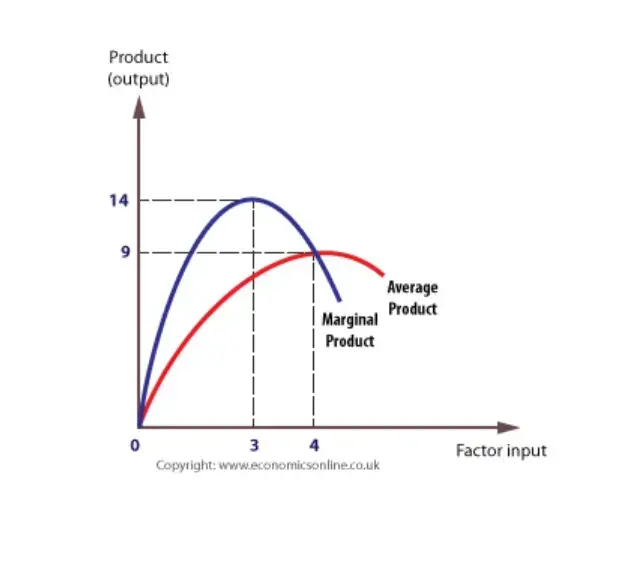
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is. In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is: D. Q1Q3. 3. In the diagram, total product will be at a maximum at: A. Q3 units of labor. 4. Use the following data to answer the question: Refer to the data. The average product (AP) when two units of labor are hired is: Marginal product: may initially increase, then diminish, and ultimately become negative. The law of diminishing returns describes the: relationship between resource inputs and product outputs in the short run. The total output of a firm will be at a maximum where: MP is zero. In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is: Q1Q3. Diminishing Marginal Returns Diagram. As we can see from the diagram, at 3 workers, the gap between marginal profit and marginal cost is at its maximum. However, at 4 workers, the marginal cost of producing an additional unit starts to become more expensive. At this point, we start to see diminishing marginal returns. The marginal cost curve is generally upward-sloping, because diminishing marginal returns implies that additional units are more costly to produce. We can see small range of increasing marginal returns in the figure as a dip in the marginal cost curve before it starts rising. Figure 6.7: Marginal Cost
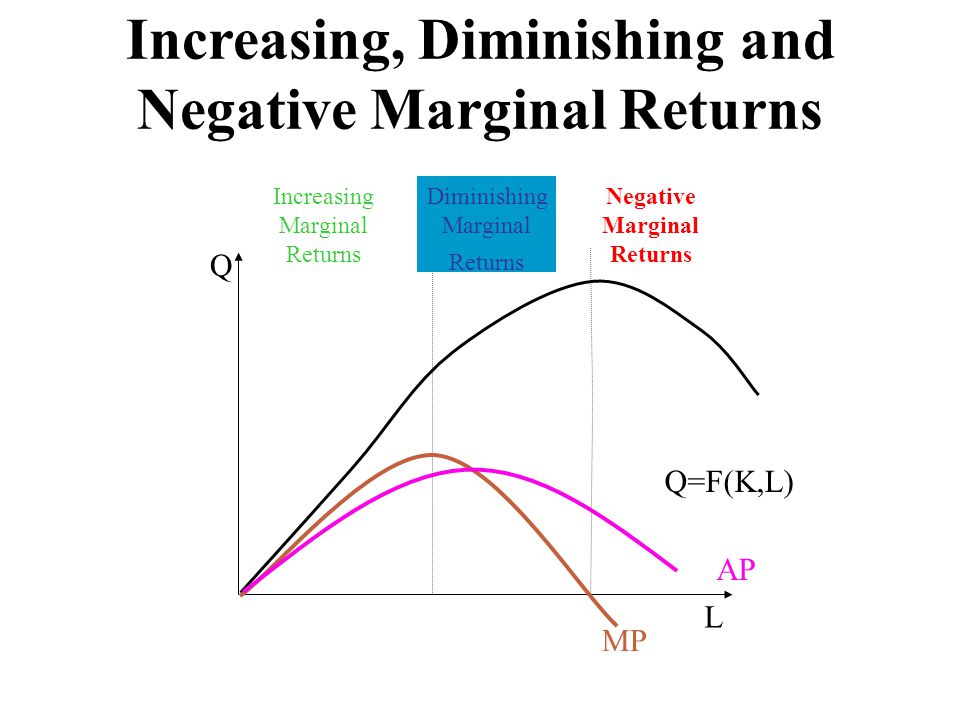
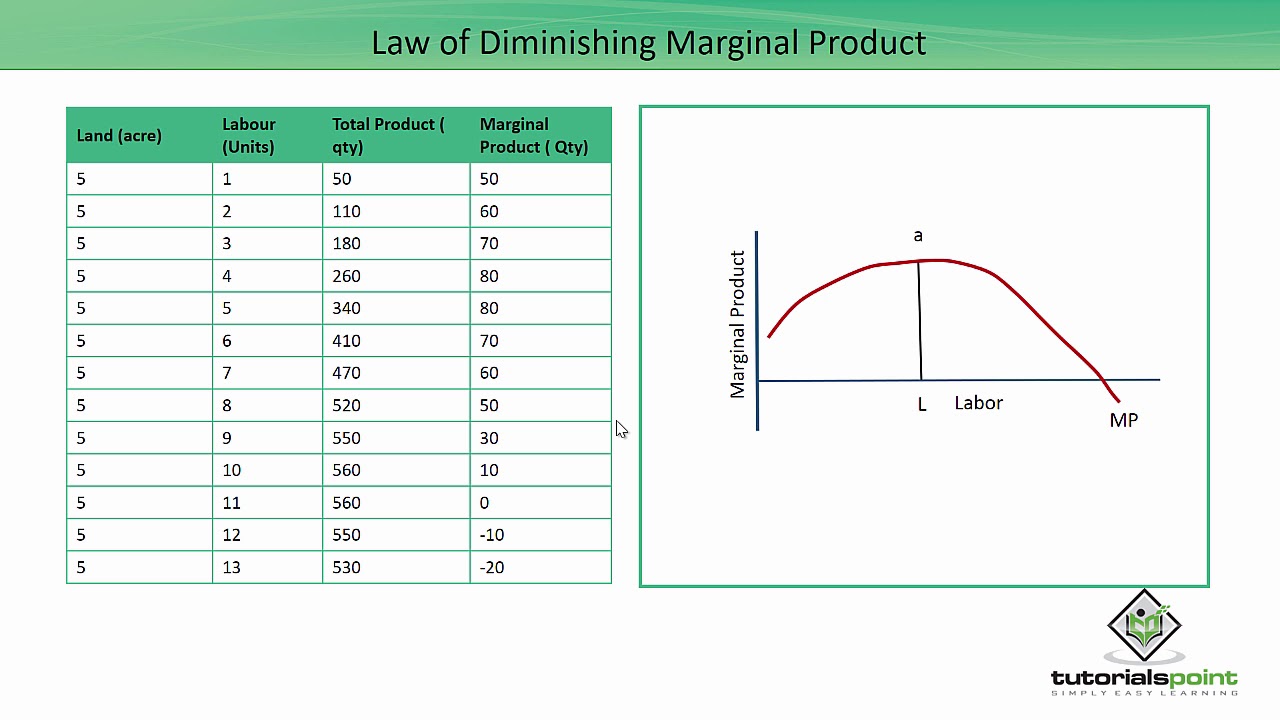
Dec 07, 2019 · Production and Costs Important Questions for Class 12 Economics Concept of Cost Function. 1.Cost It refers to the expenditure incurred by a producer on the factor as well as non-factor inputs for a given amount of output of a commodity.. 2.Cost Function A cost function shows the functional relationship between output and cost of production. It is given as Stage II: Diminishing Returns. Throughout the stage of diminishing returns, the total product keeps on increasing. However unlike the stage of increasing returns, here the total product increases at a diminishing rate. This happens because the marginal product falls and becomes less than the average product, which also sees a downwards slope. Stage II - The TPP continues to increase but at a diminishing rate. However, the increase is positive. Further, the MPP decreases with an increase in the number of units of the variable factor. Hence, it is called the stage of diminishing returns. In this example, Stage II runs between four to six units of labour (between the points L and M). Increasing returns mean lower costs per unit just as diminishing returns mean higher costs. Thus, the law f of increasing return signifies that cost per unit of the marginal or additional output falls with the expansion of an industry. As more and more units of the commodity are produced, the cost per unit goes on steadily falling.
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is: a. 0Q3.b. 0Q2.c. Q1Q2.D. Q1Q3.6. If you operated a small bakery, which of the following would be a variable cost in the short run?a. Baking ovens.b. Interest on business loans.c. Annual lease payment for use of the building.d. Baking supplies (flour, salt, etc.).7. Diminishing marginal returns is an effect of increasing an input after an optimal capacity has been reached leading to smaller increases in output. Returns to scale measures the change in ... Diagram of diminishing returns . In this example, after three workers, diminishing returns sets in. After employing 4 workers or more - the marginal product (MP) of the worker declines and the marginal cost (MC) starts to rise. Difference between diminishing returns and dis-economies of scale Law of Diminishing Returns (Explained With Diagram) Law of diminishing returns explains that when more and more units of a variable input are employed on a given quantity of fixed inputs, the total output may initially increase at increasing rate and then at a constant rate, but it will eventually increase at diminishing rates. In other words ...
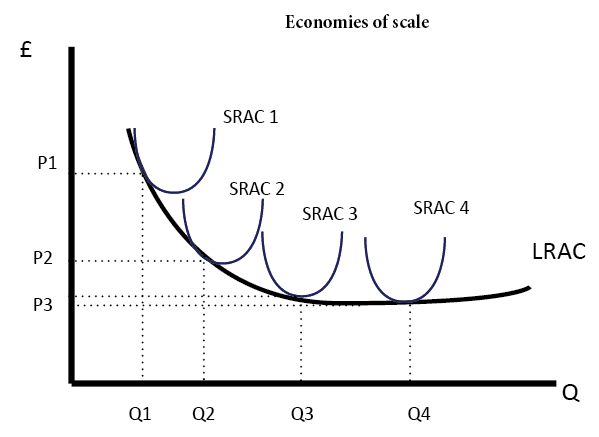
According to the law of constant returns when a firm employs more and more factors, output increases at a constant rate. Therefore, the average cost curve as well as marginal cost curve remains parallel to horizontal axis. This can be made clear with the help of diagram 13. In the diagram 13 output has been measured on OX- axis while costs on ...
At some point, diminishing marginal returns sets in and the marginal product of ... In the airline industry, for example, fixed costs range from 40 to 70 ...
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns: The law of diminishing marginal returns is a law of economics that states an increasing number of new employees causes the marginal product of another employee ...
Stage 2: Stage two is the period where marginal returns start to decrease. The output increases at a decreasing rate, and the average and marginal physical product are declining. In other words we can say that each additional variable input will still produce additional units but at a decreasing rate due to the law of diminishing returns.
Over this range marginal product is diminishing. 4. Finally, a point will be reached beyond which total output itself will actually fall, indicating a negative marginal product. In Fig. 13.4, this occurs for employment levels greater than 5.6. iii. The Average-Marginal Relationship: There is also a very close relation between MP L and AP L ...
Stage two is the period where marginal returns start to decrease. Each additional variable input will still produce additional units but at a decreasing rate. This is because of the law of diminishing returns: Output steadily decreases on each additional unit of variable input, holding all other inputs fixed.

How To Counter The Law Of Diminishing Marginal Returns For Your Business Web India Market Website Design Software Development Company In Delhi
Law of diminishing marginal returns at a certain point employing an additional factor of production causes a relatively smaller increase in output. In the diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. Micro econ ch12 25 terms. The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is.
The point of diminishing returns refers to the inflection point of a return function or the maximum point of the underlying marginal return function. Thus, it can be identified by taking the second derivative of that return function. For example, the return function is: R = -2x 3 + 24x 2 + 50; Thus, the first and second derivatives are:
It is due to the diminishing cost conditions. v. We get a long run supply curve by joining e 1 and e 2, which is downward looking or negatively sloped. vi. It can be stated, therefore, that the long run industry supply curve under diminishing cost condition will have a negative slope.
In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is: Q1Q3. In the above diagram, total product will be at a maximum at: Q3 units of labor. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is: ... The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is. not 4.
In the diagram below, the range of diminishing marginal returns is: А. 00з. В. О2. C. Qi2 D. Qi Marginal Product Average Product Q2 Inputs of Labor o Marginal and Average Product Refer to the short-run graph data below. The profit-maximizing output for this firm is A. above 440 units B. 440 units C. 320 units D. 100 units Total Cost Total ...
Thus, this approach might also cause an standard lower within the marginal product, and diminishing marginal returns. Also do not forget, to boom manufacturing, one desires to growth the price and other inputs, simultaneously In the diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. This law holds that as you add more workers to the ...
Over the range of diminishing marginal returns, the marginal product of the variable factor is positive but falling. Once again, we assume that the quantities ...
14) The law of diminishing returns describes the: A. relationship between total costs and total revenues. B. profit-maximizing position of a firm. C. relationship between resource inputs and product outputs in the short run. D. relationship between resource inputs and product outputs in the long run. 4 [Type text] Part 2: 1) In the above ...
In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. In the above diagram total product will be at a maximum at. Law of diminishing returns helps mangers to determine the optimum labor required to produce maximum output. B in the long run all resources are variable while in the short run at least one resource is fixed.
Also called the law of diminishing marginal returns, the principle states that a decrease in the output range can be observed if a single input is increased over time. The word 'diminishing' suggests a reduction, and this reduction takes place due to the manner in which goods are produced.
MC When the marginal cost (MC) increases, it SRAC Q means the cost of producing one additional unit of the good becomes higher. The MC rises due to diminishing marginal returns. This is because if we are gaining less output from raw materials (factors of production e.g. labour), this means we need more of it to produce the next unit,
Q (1) Explain and illustrate with diagrams the differences between diminishing marginal returns and decreasing economies of scale and cite causes and examples. Ans. The law of diminishing returns is also called the law of variable proportion, as the proportions of each factor of production employed keep changing as more of one factor is added.
The marginal cost is shown in relation to marginal revenue (MR), the incremental amount of sales revenue that an additional unit of the product or service will bring to the firm. This shape of the marginal cost curve is directly attributable to increasing, then decreasing marginal returns (and the law of diminishing marginal returns).

Capital Requirements Monetary Policy And Aggregate Bank Lending Theory And Empirical Evidence Thakor 1996 The Journal Of Finance Wiley Online Library

Economic Diversification In Africa How And Why It Matters Carnegie Endowment For International Peace
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Law_of_Diminishing_Marginal_Productivity_Oct_2020-01-d3c30a9c6ba442b9bccc7b99158251e3.jpg)
/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)





.jpg)













Comments
Post a Comment